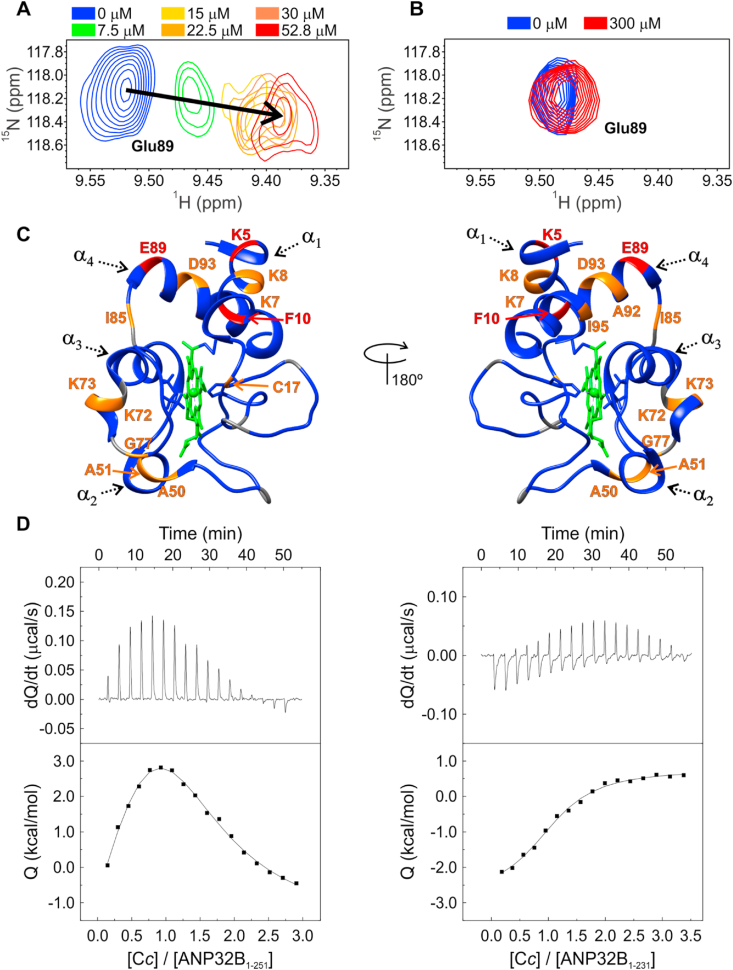
Fig. 4.
ANP32B low complexity acidic region drives Cc:ANP32B complex formation. Detailed view of the superimposed [1H–15N] 2D HSQC spectra of 15N-labelled Cc upon titration with increasing concentrations of ANP32B1-251 (A) and ANP32B1-161 (B). Color code for ANP32B1-251 concentration is shown in the panels. Displayed resonance corresponds to Cc Glu89 amide group. (C) Ribbon representation of Cc colored according to ΔδAVG of the amide signals upon titration with ANP32B1-251. ΔδAVG categories are colored as follows: small <0.050 ppm (blue), medium 0.050–0.075 ppm (orange) and large >0.075 ppm (red). Prolines and unassigned residues are in grey, and the heme group is in green. Cc molecule is rotated 180° around vertical axes in each view. The four alpha-helices of Cc—named from α1 to α4— are indicated by dashed arrows. Cc PDB ID: 1J3S [47] (D) ITC analysis of the interaction between reduced Cc with ANP32B1-251 (left panel) and ANP32B1-231 (right panel). Thermograms and binding isotherms are shown in the upper and lower panels, respectively. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)