Fig. 4.
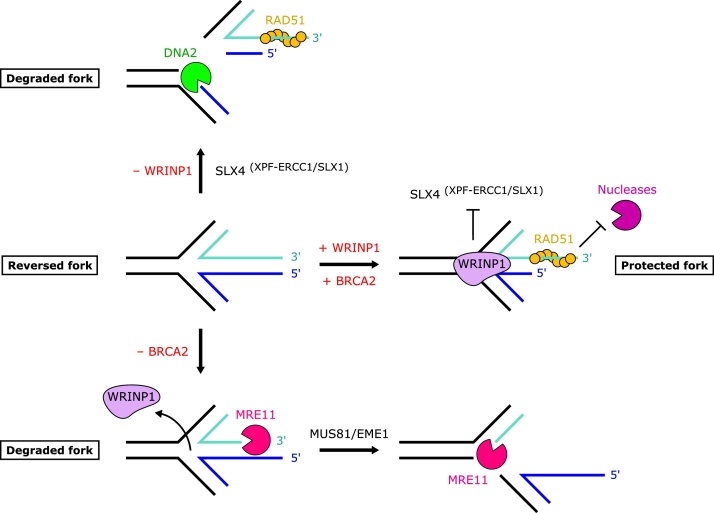
WRNIP1 protects replication forks in a distinct manner to BRCA2. WRNIP1 is able to bind the four-way junction of a reversed replication fork and protects it from cleavage by SLX4(XPF−ERCC1/SLX1). In the absence of WRNIP1, cleavage of the fork by SLX4(XPF−ERCC1/SLX1) creates a substrate for nascent DNA degradation by DNA2. In contrast, following loss of BRCA2, fork protection is compromised in a distinct manner, whereby initial degradation by MRE11 enables cleavage of the fork by MUS81/EME1, subsequently facilitating extensive MRE11-mediated degradation of DNA.