Fig. 5.
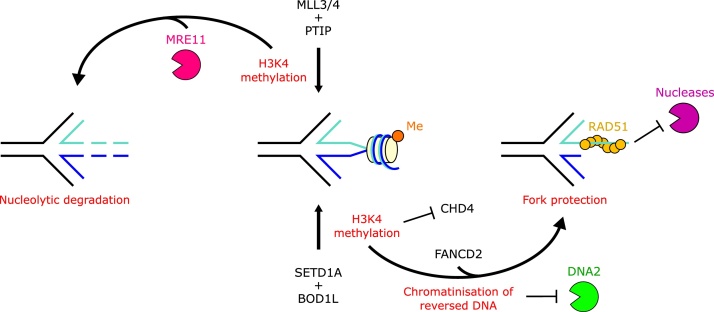
H3K4 methylation can promote distinct outcomes at reversed replication forks depending on the cellular context. In BRCA2-deficient cells, H3K4 methylation by MLL3/4 and PTIP promotes MRE11 recruitment to stalled replication forks and contributes to nascent DNA degradation. In contrast, H3K4 methylation by SETD1A and BOD1L promotes replication fork protection, by preventing the recruitment of CHD4 to the fork, and enhancing the histone chaperone function of FANCD2 to facilitate the chromatinisation of the reversed nascent strand and prevent DNA2-mediated degradation.