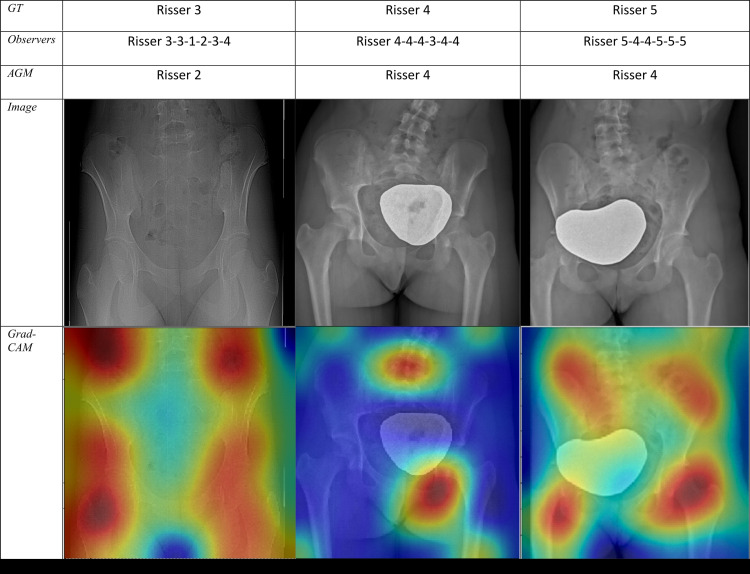
Figure 5b:
(a) Sample radiographic images graded by the automatic grading method (AGM). First row: Correctly classified. Second row: Misclassified by one grade. Third row: Misclassified by two grades. (b) Sample radiographic images. First row: ground truth (GT). Second row: Risser stage assigned by each observer. Third row: Risser stage assigned by AGM. Fourth row: Original image. Fifth row: Gradient-weighted class activation mapping (Grad-CAM) highlighting the AGM’s most important regions of images. The color map scales from red (most discriminant) to blue (least discriminant).