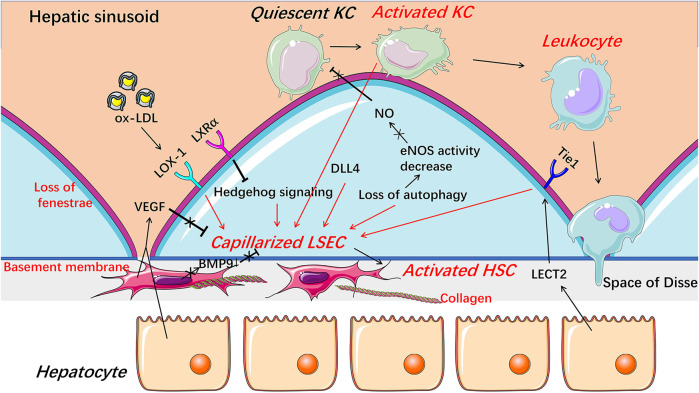
FIGURE 3.
Capillarization and endothelial dysfunction of LSECs under pathological condition. When injured, LSECs undergo capillarization represented by the loss of fenestrae and the formation of basement membrane which are involved in Hedgehog signaling, autophagy, HSCs-derived BMP9, LSECs-derived DLL4, and receptors including LOX-1, LXRα, and Tie1. The reduction of NO bioavailability is an important indicator of endothelial dysfunction and involved in the progress of the capillarization of LSECs. Capillarized and dysfunctional LSECs promote the activation of HSCs and KCs and thus promote liver fibrosis and inflammation. BMP9 Bone morphogenetic protein 9, DLL4 Delta-like ligand 4, HSC hepatic stellate cell, KC Kupffer cell, LECT2 leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin 2, LSEC liver sinusoidal endothelial cell, LXRα liver X receptor α, LOX-1 lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1, NO Nitric oxide, ox-LDL oxidized low-density lipoproteins, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor.