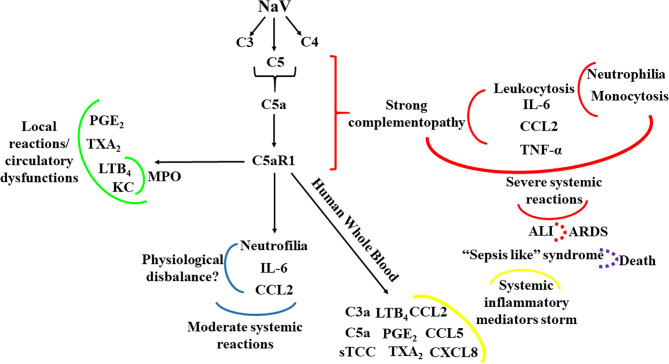
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of the contribution of the C5a-C5aR1 axis to local and systemic reactions induced by N. annulifera venom (NaV). NaV acts on complement proteins culminating in anaphylatoxins generation and sTCC assembly. C5aR1 engagement by C5a stimulates LTB4, PGE2 and TXB2 generation, which cause endothelial dysfunctions promoting vascular leakage resulting in extensive edema. In addition, the release of LTB4 and KC, triggered by C5aR1 signaling, may promote the attraction and activation of neutrophils into tissue, increasing MPO levels and potentiating local immunopathology (green lines). The systemic C5aR1 activation, stimulated by NaV sublethal dose injection, promotes moderate increase on CCL2 and IL-6 levels, as well in the neutrophil’s percentage, which could lead envenomated animals to a several physiological disbalance (blue lines). By coupling human whole blood ex vivo (yellow lines) approaches and a severe experimental mouse model of envenomation, it was detected that NaV promotes a hyperacute inflammatory reaction featured by intense systemic inflammatory mediators’ storm, induced by C5a-C5aR1 axis activation. This can evolve to a plethora of pathological conditions including ALI development (red lines) that can progress to ARDS (red dotted lines) and respiratory arrest, a common death cause in humans envenomated by N. annulifera. In addition, these inflammatory mediators can promote organ dysfunction featuring a sepsis like syndrome, which could be a death cause of the envenomated individuals (purple dotted lines).