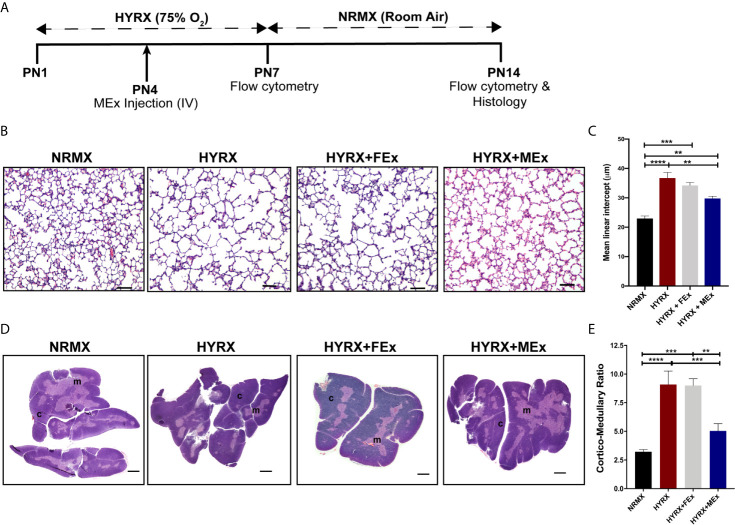
Figure 2.
MEx restores thymic morphology after HYRX-induced injury. (A) Newborn mice (FVB strain) were exposed to hyperoxia (HYRX; 75% O2) for 7 days. HYRX-mice were compared with mice that were maintained in room air (NRMX). MEx treatments were administered intravenously (IV) at Postnatal day (PN) 4. Morphological outcomes were assessed at PN14. HYRX-exposed mice were compared with mice that remained at NRMX conditions for the duration of the study and human dermal fibroblast EV (FEx)-treated mice were used as biological controls. (B) HYRX-control and FEx treated mice presented with significant alveolar simplification compared to NRMX group. HYRX-mice that received a single dose of MEx had a significantly improved lung alveolarization compared to both HYRX- and FEx-controls. Images taken at 100x magnification and scale bars = 100 µm. (C) Quantification of mean linear intercept as a surrogate of average air space diameter. (D) Harvested thymi sections were stained for hematoxylin and eosin which evidences the cortex (dark purple areas) and the medulla (light purple areas) of the thymus. Images were taken at 40x magnification. Scale bars = 1000 µm. (E) Quantification of thymic cortico-medullary ratios in NRMX, HYRX, HYRX + FEx and HYRX + MEx groups. All data represent mean ± SEM n = 8-15 for each group (data pooled from at least two independent experiments). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001.