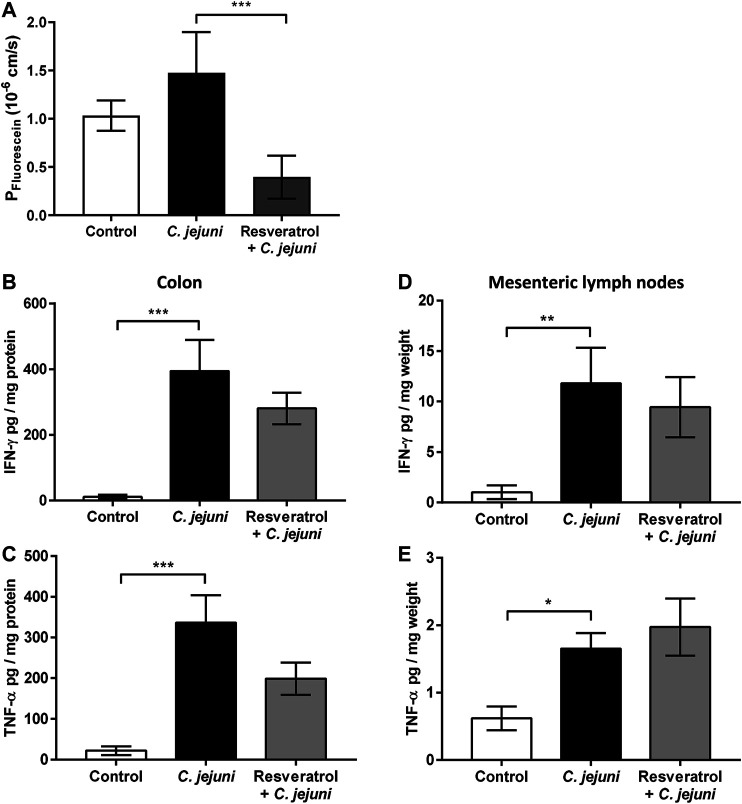
FIGURE 7.
In vivo mouse infection model and oral treatment with resveratrol. Barrier function and simulated antigen influx by fluorescein in the Campylobacter jejuni-infected mouse colon. Secondary abiotic IL-10−/− mice were infected with C. jejuni, treated with resveratrol via the drinking water and sacrificed at day 6 post-infection (A) Colon specimens of C. jejuni-infected and resveratrol treated mice were mounted into Ussing chambers and flux measurements of fluorescein were performed in mucosal to serosal direction (B and C) release of pro-inflammatory cytokines of mouse organs from colon and (D and E) mesenteric lymph nodes. Organ specimens were cultured in cell culture medium and supernatant was analyzed by Cytometric Bead Array for (B and D) IFN-γ and (C and E) TNF-α concentrations (n = 4–17, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Mann Whitney U-test).