Figure 2.
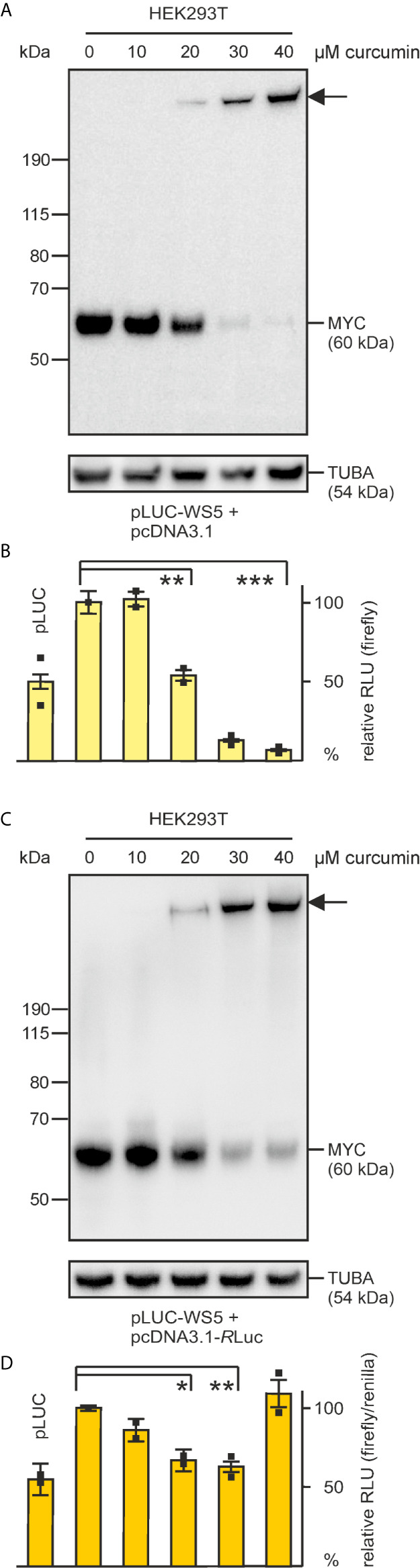
Inhibition of MYC-dependent transcriptional activation in human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293T) by increasing curcumin concentrations. The firefly luciferase reporter construct pLUC-WS5 specifying the Myc target WS5 (39) (187.5 ng) was delivered into HEK293T cells (1.5 × 105) via lipofection together with 187.5 ng of the empty pcDNA3.1 vector (A, B), or 300 ng pLUC-WS5 with 75 ng of pcDNA3.1-Rluc specifying the luciferase enzyme from Renilla reniformis (C, D). (A, C) 6 h after lipofection, curcumin was added at the indicated concentrations, and 30 h after lipofection, protein extracts were prepared. Equal amounts of protein extracts were tested for endogenous MYC expression by immunoblotting using an antibody directed against human MYC. The arrows depict the position the MYC-specific high molecular weight protein. As a loading control, α‑tubulin (TUBA) expression analysis was included. (B, D) luciferase activities were measured from cell extracts prepared 30 h after lipofection (n = 2). A 100% activity corresponds to 1.0 × 106 relative light units (RLU) in (B). Firefly and renilla luciferase activities were determined in (D) and firefly values normalized using the renilla values as a reference (n = 2). In the applied HEK293T cells, the cotransfection of pcDNA3.1 or pcDNA3.1-Rluc with the empty firefly luciferase reporter pLUC resulted into elevated basal activities, which has not been observed in other cell lines (33, 36). Vertical error bars in (B, D) indicate standard deviations (SD) from triplicates. Statistical significance was assessed by using a paired Student t-test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005).
