Fig. 3.
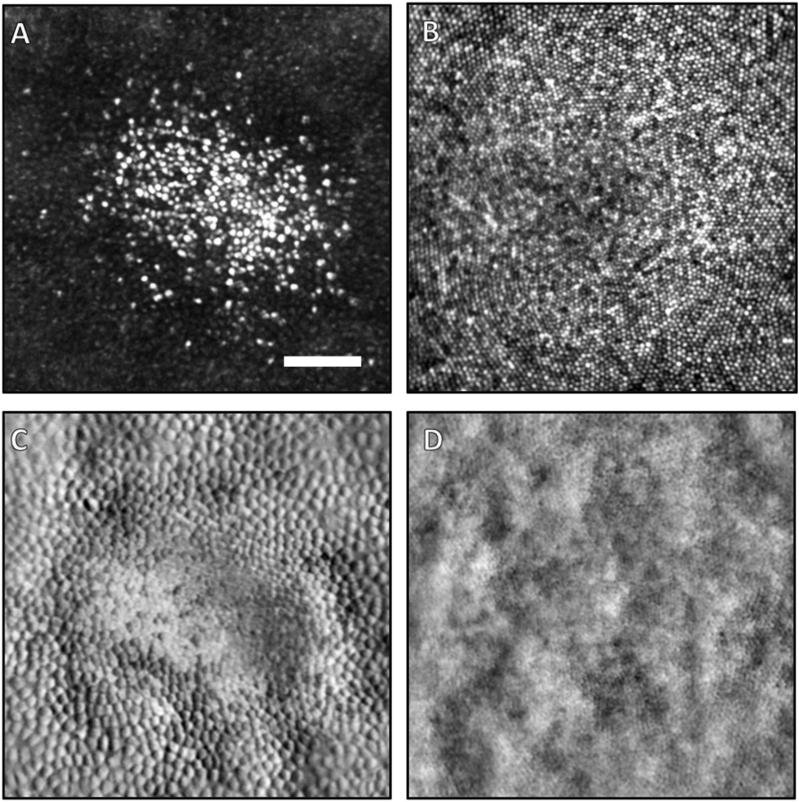
AOSLO images (250 μm × 250 μm) of the cone photoreceptor mosaic in the central fovea of the right eye of the patient (A,C) and a healthy control (B,D). Both confocal scans (A,B) and non-confocal split detection images (C,D) are shown. In the patient, a small island of foveal cones are spared and have bright reflectivity compared to the surrounding cones (A). The patient's cones are also larger than the typical foveal cones of a normal subject (B). The most central cones of a typical healthy fovea are barely resolvable with this instrument. Simultaneously acquired non-confocal split-detection images, which normally depict the cone inner segment mosaic, of the patient (C) and healthy control (D) are shown. In the patient, the inner segments immediately outside the area of spared foveal cones appear larger and with much higher contrast than the fully intact cones (C). This difference in size and contrast is also apparent when comparing these inner segments to those of the healthy control (D). This increased contrast is an effect of the elevated height of these cones above the RPE, which amplifies the contrast in non-confocal split-detection imaging. The scale bar in (A) is 50 μm.