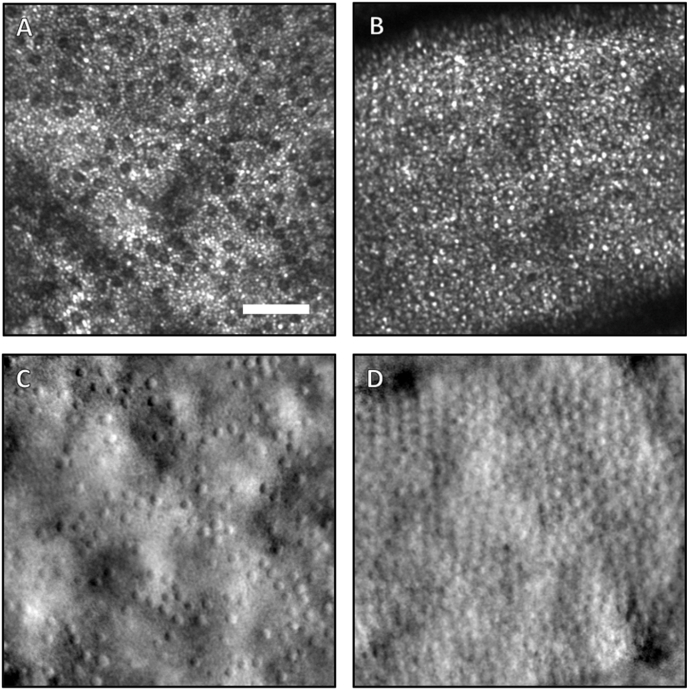
Fig. 5.
AOSLO scans taken at retinal eccentricities of 10° nasal from the fovea in the right eye of both the patient (A,C) and the healthy control (B,D). The confocal scans are shown above (A,B) and the non-confocal split detection images are shown below (C,D). The patient has a degree of cone photoreceptor inner segment preservation in this nasal region which is just outside the macular lesion seen on fundus photography in Fig. 1. There is, however, a lower spatial density of these cells overall when compared to a similar location in the healthy control subject eye. Rod photoreceptors, which are smaller than cones, populate most of the area imaged. The rod size appears larger in (A) and their inner segments are more visible in (C) compared to a matched area in the healthy control subject's eye (D). In the normal control, the rod photoreceptor inner segments are not discernible from the large cones. Of note, the large dark lines in (A), (B), and (D) indicate shadow artifacts from large blood vessels and are normal features in AOSLO images. All scans are 250 μm by 250 μm, and the scale bar in (A) indicates a length of 50 μm.