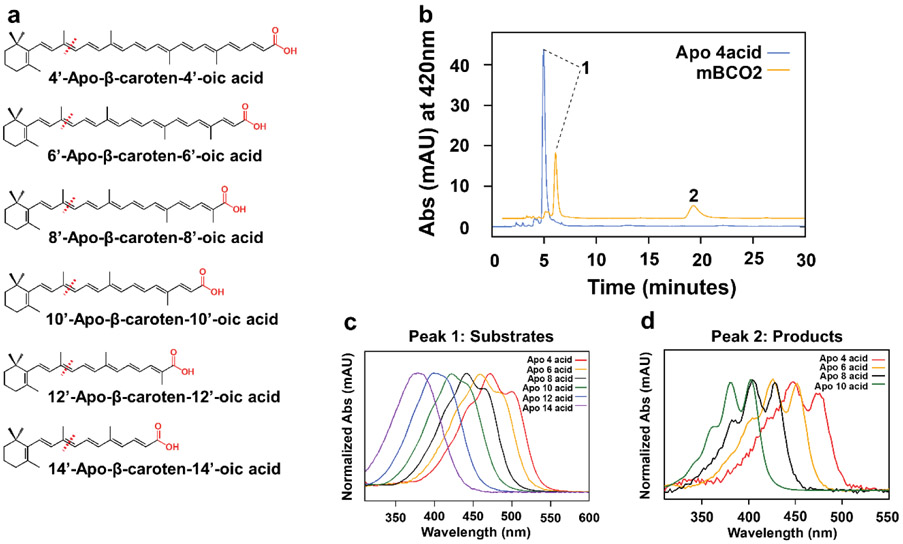
Figure 2.
mBCO2 converts β-apo-carotenoic acids with various chain length. a) Chemical structures of the β-apo-carotenoic acid substrates with different chain length. Expected cleavage sites are indicated with red dashed lines. The carboxylic end groups are highlighted in red. b) Representative HPLC of lipid extracts of reactions with β-apo-4’-carotenoic acid incubated in the presence (orange trace) and absence (blue trace) of mBCO2. Peak 1 is β-apo-4’-carotenoic acid and peak 2 is 10-Oxo-10,4’-diapocarotene-4’-oic acid. c) Representative UV-visible absorption spectra of β-apo-carotenoic acid substrates. d) Representative UV-visible absorption spectra of diapocarotenoid products from enzyme assays with mBCO2.