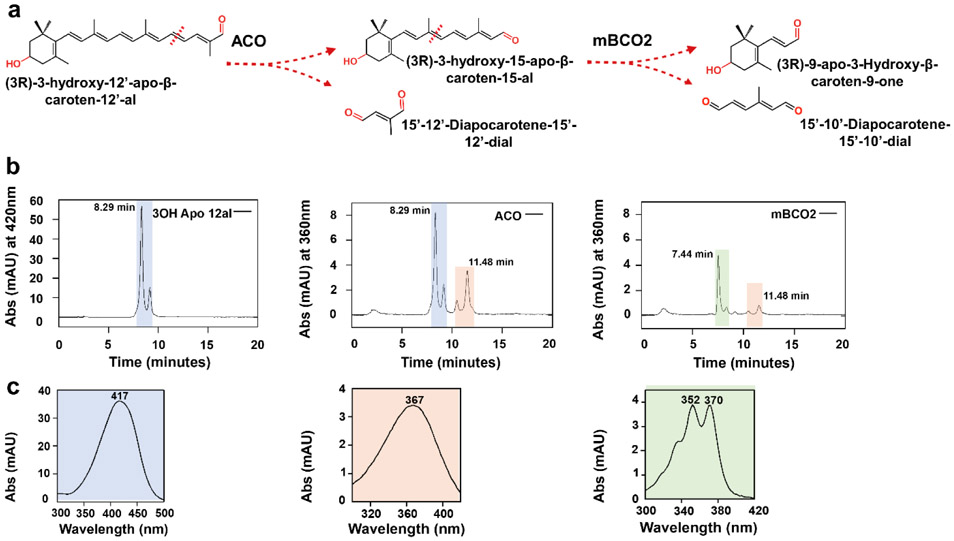
Figure 3.
mBCO2 converts 3-hydroxy-retinal after being generated by ACO. a) Reaction scheme for the successive conversion of 3-hydroxy-β-apo-12’-carotenal by ACO to 3-hydroxy-retinal, followed by the conversion of 3-hydroxy-retinal to 3-hydroxy-β-ionone. b) HPLC traces of enzyme assays with ACO and mBCO2. Left panel displays the HPLC trace at 420 nm of the 3-hydroxy-β-apo-12’-carotenal substrate (retention time, 8.29 min); middle panel displays HPLC trace at 360 nm of an enzyme assay with 3-hydroxy-β-apo-12’-carotenal and ACO which results in 3-hydroxy-retinal (retention time, 11.48 min) formation; right panel displays HPLC trace at 360 nm of an enzyme assays in which the 3-hydroxy-retinal produced by ACO was incubated in the presence of mBCO2. Note that this incubation results in the disappearance of the 3-hydroxy-retinal peak. Additionally, 10’,10-apocarotene-dialdehyde (retention time, 7,44 min) is produced by the conversion of the remaining 3-hydroxy β apo-12’-carotenal substrate. c) UV-Visible spectra of peak 1, 3-hydroxy-β-apo-12’-carotenal, peak 2, 3-hydroxy-retinal and peak 3, 12’,10-apocarotene-dialdehyde. The cis isomer of 3-hydroxy-β-apo-12’-carotenal substrate elutes next to the major substrate peak.