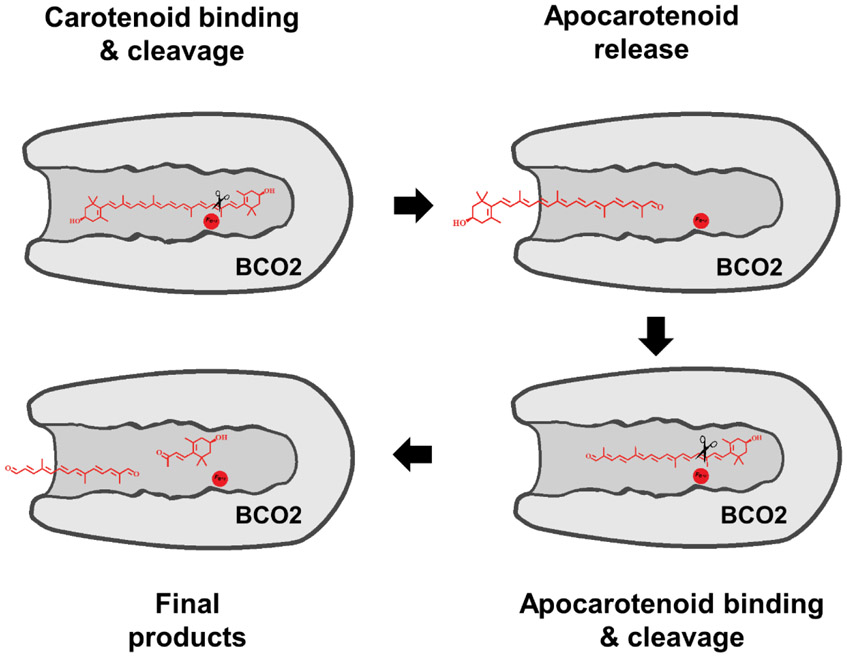
Figure 7.
Cartoon of the different steps of carotenoid cleavage by BCO2. The carotenoid molecule enters the substrate-binding tunnel. Cleaves at the 9,10 double bond results in the removal of one ionone ring site and the formation of an apocarotenoid. The apocarotenoid product leaves the substrate-binding cavity. The apocarotenoid then reenters the substrate-binding cavity in reverse direction followed by cleavage at the 9’,10’ double bond position. The results in the removal of the second ionone ring site and the formation of a diapocarotenoid product.