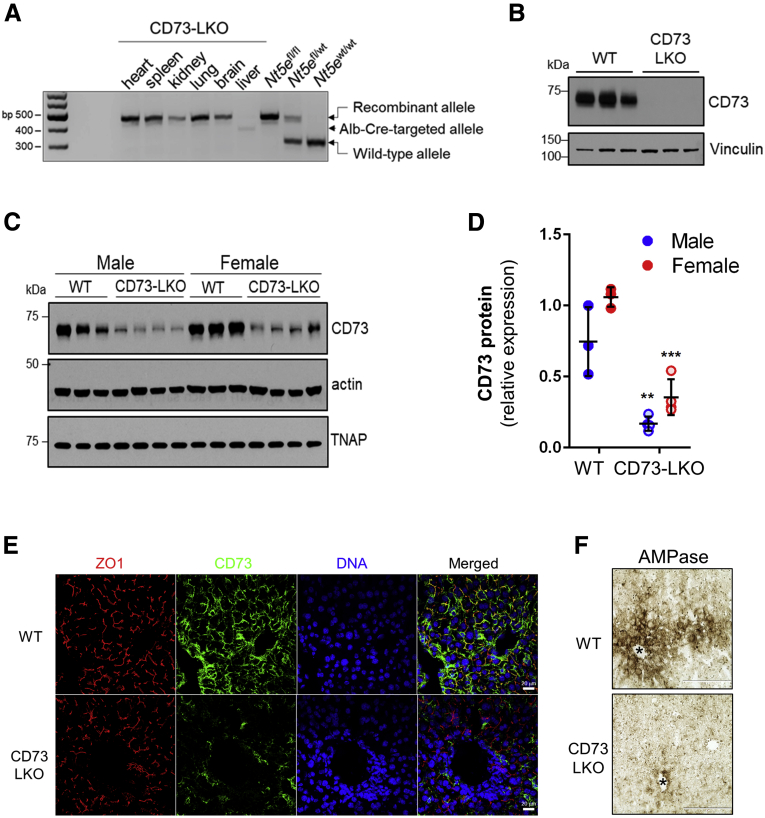
Figure 2.
Generation of liver-specific CD73-LKO mice. (A) PCR analysis of Nt5e generated a 349-bp fragment from the Cre-targeted allele in the CD73-LKO mouse liver. Nt5e(wt/wt), Nt5e(fl/wt), and Nt5e(fl/fl) mice are controls. Representative immunoblots of CD73 in (B) primary hepatocytes, and (C) in total liver lysates from male and female WT and CD73-LKO mice. Actin and tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP) immunoblots serve as controls. (D) Semiquantitative analysis of CD73 protein expression based on immunoblot band intensities in panel C. ∗∗P < .01, ∗∗∗P < .001, 2-way analysis of variance. Error bars represent SD. (E) Immunofluorescence staining for CD73 (green), tight junction protein zonula occludens 1 (ZO1) (red), and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-stained DNA (blue) on frozen liver tissue sections from WT (top) and CD73-LKO (bottom) mice. Scale bar: 20 μm. (F) AMPase activity in WT and CD73-LKO mice using formalin-fixed liver tissue sections. The brown deposits indicate ecto-AMPase activity in the presence of AMP. Stars indicate the central vein. Scale bar: 400 μm.