Fig. 2.
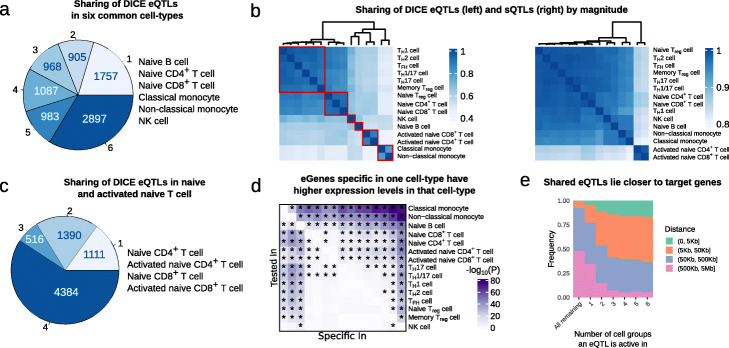
Sharing of eQTLs and sQTLs using mash. a Estimated number of cell types in which eQTLs are inferred to be active out of six DICE cell type groups according to mash. These estimates of sharing are much higher than that from the original study [8]. b Sharing of eQTLs (left) and sQTLs (right) by magnitude (Fold difference in QTL effect size less than 2). Red square: cells were grouped into six clusters based on eQTL sharing, which resulted in the following groups: (i) Naïve T cells, (ii) Memory and Effector T cells, (iii) Monocytes, (iv) activated T cells, (v) B cells, and (vi) NK cells. c Estimated number of cell types in which eQTLs are inferred to be active among naïve and activated naïve T-cells from DICE. d Heatmap showing - log10p values of a differential gene expression analysis that compared the expression level of cell type-specific eGene in the discovery cell type to the expression levels of the eGene in the other 14 cell types. e Distance between eQTLs and their target genes stratified by the number of cell groups in which the eQTL is active. To obtain the six cell groups, we grouped the 15 cell types based on similarity in their mash effect sizes as described in b