Figure 8. Determining Speaker Selectivity in the Multi-talker Condition.
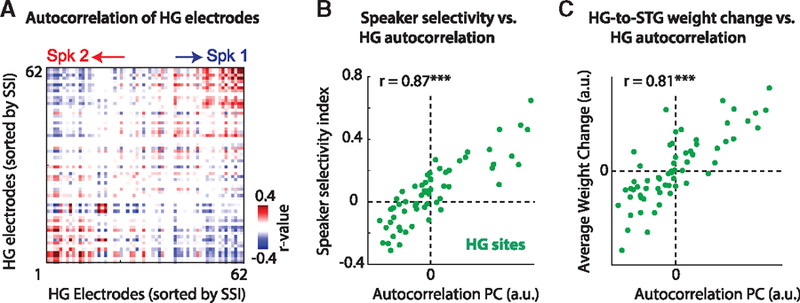
Given only the representation of the mixture in HG, sites that are selective for either speaker can be determined by obtaining the correlation structure (temporal coherence) of the responses.
(A) The correlation between all HG sites sorted according to their SSI.
(B) Decomposing the correlation matrix in (A) using principal-component analysis (PCA) permits the acquisition of a single number for each site. The large correlation (r = 0.87) with the corresponding SSI for each electrode demonstrates that the SSI can be obtained from the multi-talker responses alone.
(C) Similarly, the weights from HG to STG (HGRF) in the multi-talker condition can be determined from the same PCA analysis (r = 0.81; cf. Figure 6D).
