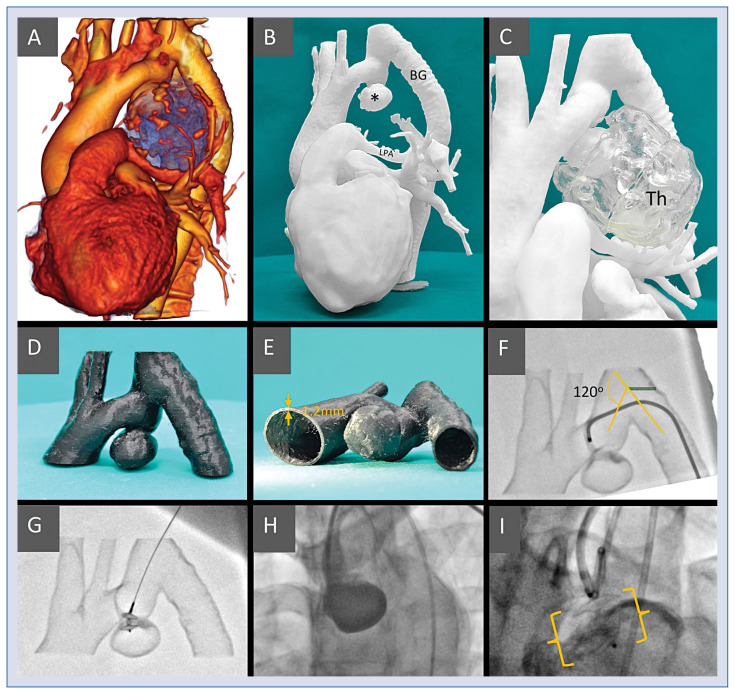
Figure 1.
A. Volume rendering of the computed tomography left antero-lateral aspect; the blue area represents the thrombotic mass with numerous calcifications on the surface; B. Model I, active aneurism (*), bypass-graft (BG) and the compressed left pulmonary artery (LPA) are clearly visible; C. Model I including the thrombotic part of the aneurismal mass (Th) made separately of translucent material; D, E. Model II — region of interest, hollow vessels for simulation and training made of semi-flexible material with 1.2 mm wall thickness to ensure model printability and durability; F. The simulated procedure from the femoral access, it was difficult to pass through the 120 degree angle to reach the implantation site; G. The simulated procedure from the left radial access, a straight route to the aneurism, the device is introduced to the implantation site; H. The treatment procedure — the sheath introduced from left radial site, secondary access from femoral to inject contrast medium. ADO II at the implantation site; I. The treatment procedure — the sheath introduced from left radial site, secondary access from femoral to inject contrast medium. ADO II at the implantation site.