Figure 4. TP53 mutational patterns in UTUC stratified by arseniasis grading in Taiwan.
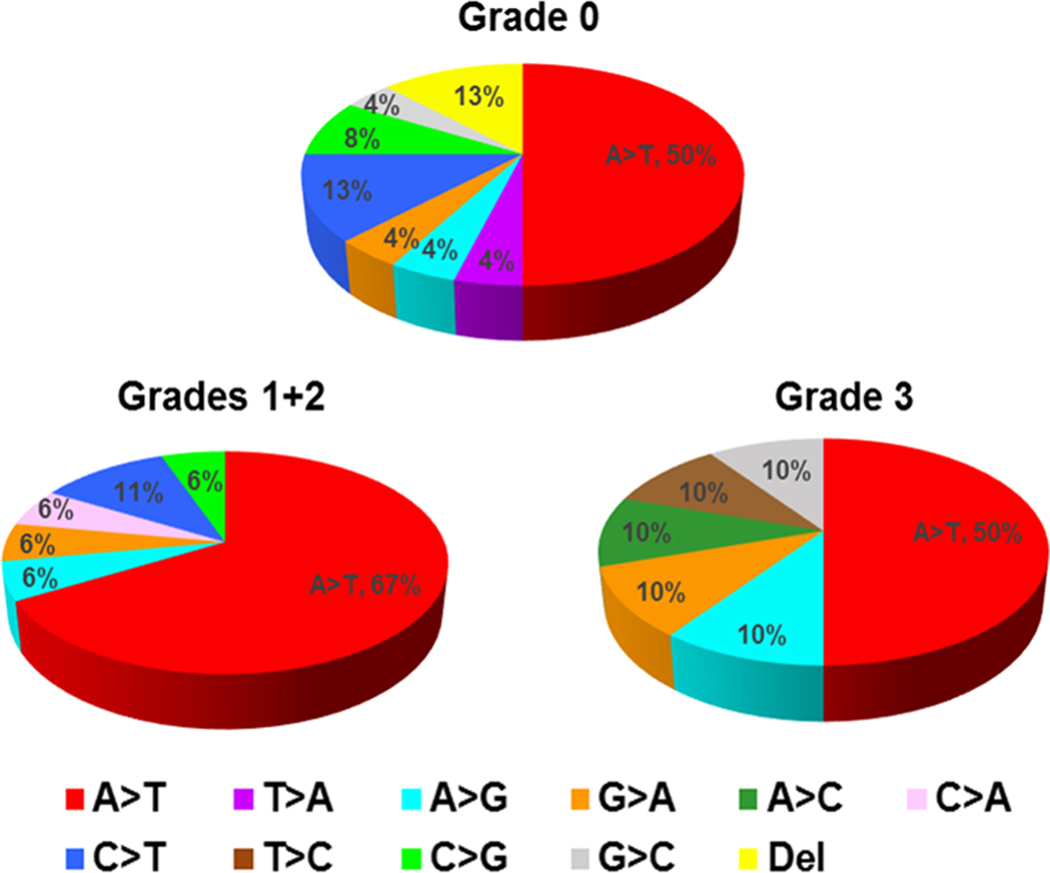
Arseniasis grades were classified from 0 (least exposure) to 3 (highest exposure).(14,15) The most common mutation for all arseniasis grades was the A>T transversion, which is part of the signature mutation for aristolochic acid carcinogenesis and suggests that an etiology other than arseniasis may play a role in cancer development.
