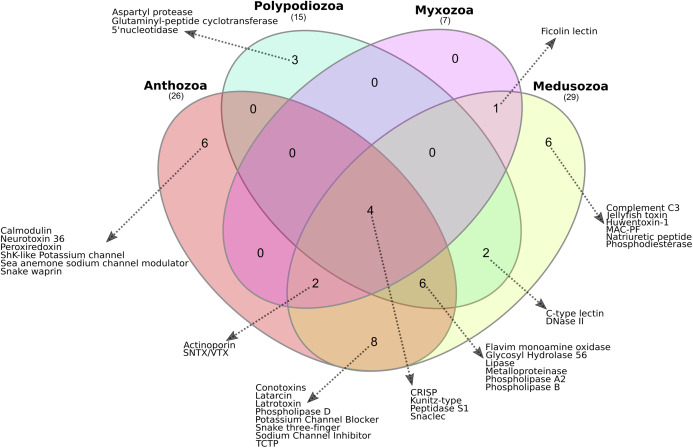
Figure 3. Comparison of the cnidarian putative venom proteomes.
Venn diagram showing the number of putative toxin protein families shared among Polypodiozoa (Polypodium hydriforme), Myxozoa (Buddenbrockia plumatellae, Myxobilatus gasterostei and Sphaerospora elegans) and entirely free-living cnidarians (Anthozoa and Medusozoa). Overall, 10% (4/38) of the putative toxin protein families were shared by all groups. Only 39% (15/38) of the putative toxin protein families were unique to a single taxon, and Anthozoa and Medusozoa have 32% of unique putative toxin protein families (12/38), with no putative toxin protein families that were unique to Myxozoa. Aspartyl peptidase was unique to Polypodium hydriforme having never been described previously in the predicted venom of any cnidarian.