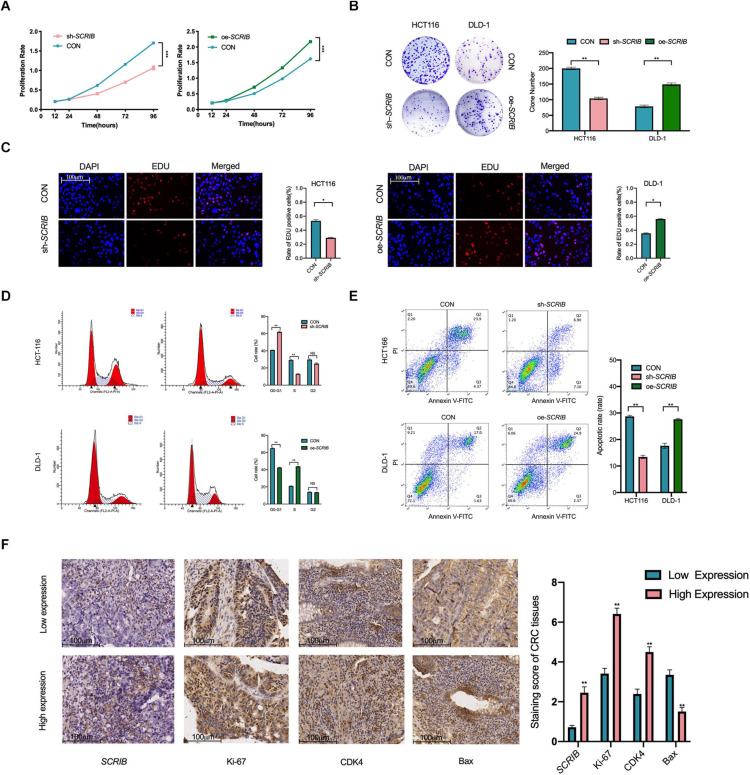
FIGURE 3.
SCRIB promotes CRC cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in vitro. (A) Cells were seeded in 96-well plates after transfection with oe-SCRIB and sh-SCRIB and the corresponding empty vectors, and the cell number was assessed on days 1–4 using CCK-8 assays. The knockdown of SCRIB suppressed the proliferation of HCT116 cells, whereas the overexpression of SCRIB promoted the proliferation of DLD-1 cells. (B) Effect of overexpression or knockdown of SCRIB on the colony formation ability of CRC cells; representative graphs are shown. (C) EdU immunofluorescence staining confirmed the function of SCRIB in the proliferation of CRC cells, scale bars: 100 μm. (D) Flow cytometry showing significant increases or decreases in the proportion of HCT116 cells in the G1 or S phase, respectively, when SCRIB was knocked down. In the SCRIB-overexpressing DLD-1 cells, the number of cells in the G1 or S phase decreased or increased, respectively. (E) The apoptotic rates (LR + UR) of transfected cells were detected by flow cytometry (Q2 + Q3). LR, early apoptotic cells; UR, terminal apoptotic cells. (F) Immunohistochemical staining of Ki-67, CDK4 and Bax was performed, and their expression was compared between SCRIB high-expressing CRC tissues and SCRIB low-expressing tissues, scale bars: 100 μm. The data are shown as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments, *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.