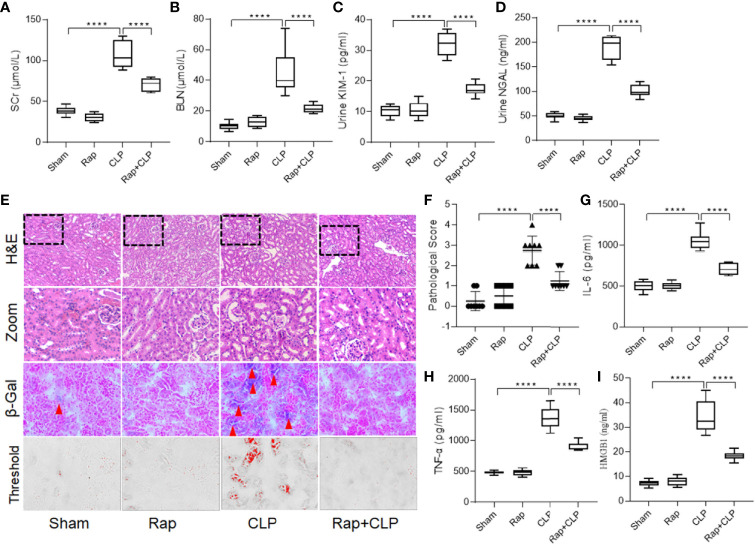
Figure 2.
Rapamycin restores renal function and attenuates septic inflammatory response. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with or without rapamycin 1 mg/kg i.p. for 1h before CLP and were sacrificed at the time point of 18-h after surgery. Renal function alternation, renal necrosis and inflammatory cytokines were detected. (A–D) levels of SCr, BUN, urinary KIM-1 and NGAL among the four groups. (E) Renal damage and senescence of rats among the four groups (H&E; scale bar 100 μm). (F) Kidney histopathology evaluation scores among the four groups. (G–I) levels of IL-6, TNF-α and HMGB1 in kidneys among the four groups. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 8). ****p < 0.0001; CLP, cecal ligation and puncture; H&E, hematoxylin–eosin staining; SCr, serum creatinine; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; KIM-1, kidney injury molecule-1; NGAL, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin; IL-6, interlecukin-6; IL-8, interlecukin-8; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha.