Figure 4.
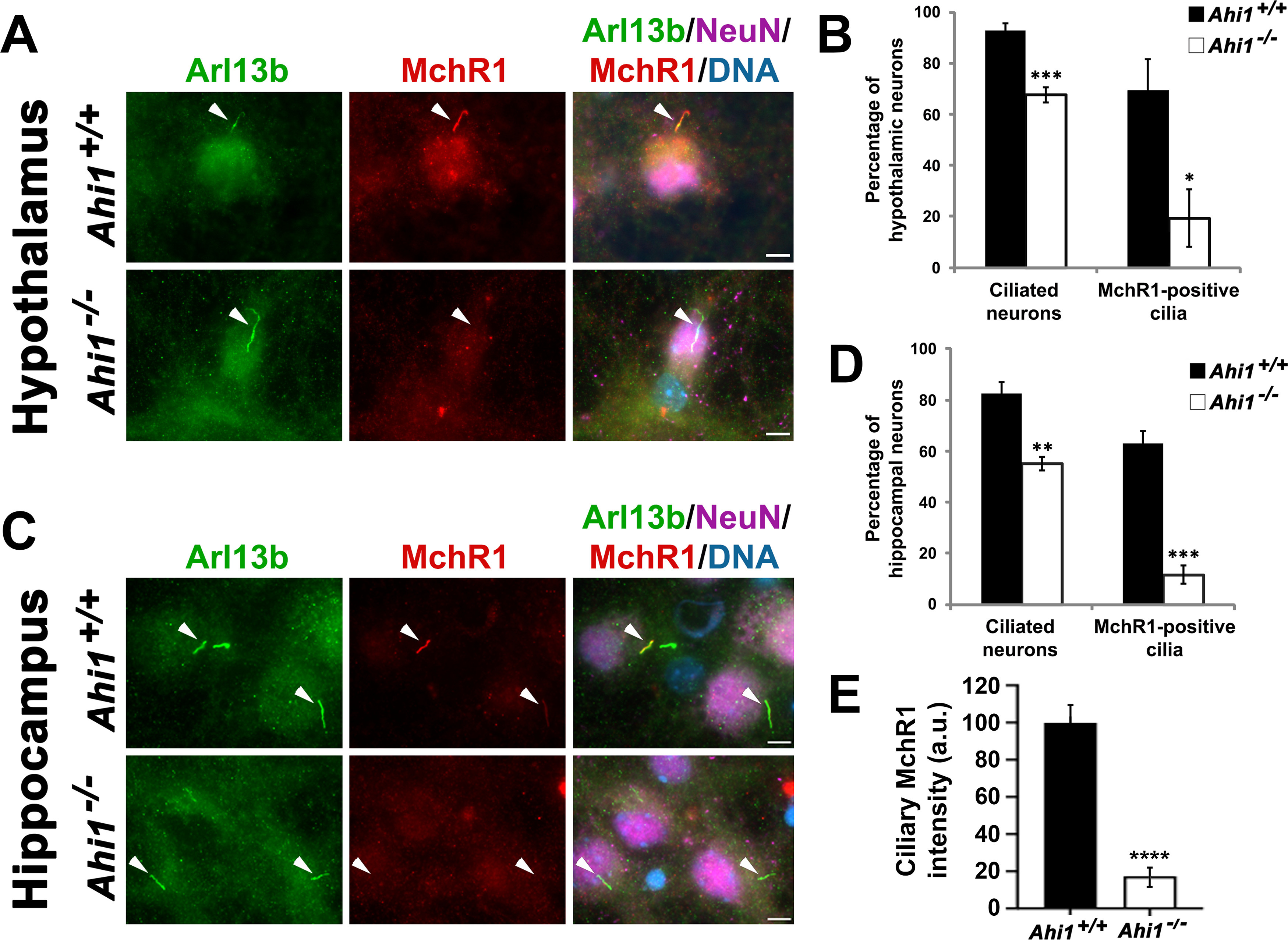
Lack of Ahi1 reduces ciliary trafficking of MchR1. Subcellular distribution of the MchR1 in hypothalamic (A) and hippocampal (C) neuronal cultures isolated from Ahi1+/+ and Ahi1–/– mice. Cells were co-stained with MchR1 (red) and NeuN (magenta), and primary cilia were immunolabeled by Arl13b (green). DNA was visualized with Hoechst 33258 (blue). White arrowheads indicate primary cilia presence. Co-localization of Arl13b and MchR1 labeling was observed in Ahi1+/+ neurons. However, most Ahi1–/– neurons lacked MchR1 immunoreactivity at primary cilia that were Arl13b-positive. Scale bar: 5 μm. Percentage of hypothalamic (B) and hippocampal (D) neurons with Arl13b-positive and MchR1-positive cilia from Ahi1+/+ and Ahi1–/– cultures; n > 100 NeuN positive cells/genotype (n ≥ 4 per tissue/genotype). E, Graph showing MchR1 integrated intensities at primary cilia (which were longer in Ahi1–/– neurons) normalized to Ahi1+/+ values in both Ahi1+/+ and Ahi1–/– neurons (n > 12 neural cells, across 4 litters). Error bars represent SEM. Significance was determined by unpaired two-tailed t tests (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005, ****p < 0.00005).
