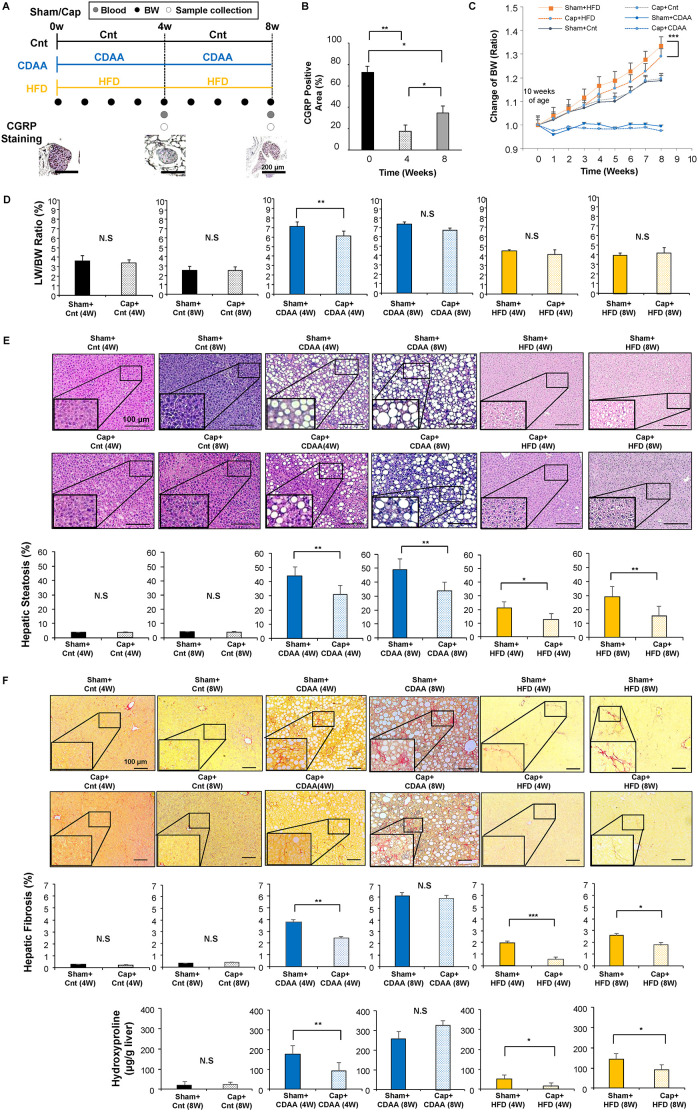
Fig. 1.
Effect of autonomic neural signal transduction on NAFLD/NASH mice models. (A) Experimental design. The mice were divided into 12 groups (n=6-8 mice per group): Sham plus Cnt (4W), Sham plus Cnt (8W), Sham followed by Cnt chow diet fed for 4 or 8 weeks; Cap plus Cnt (4W), Cap plus Cnt (8W). Direct topical application of capsaicin was used to deafferentate the afferent sympathetic nerve (Cap) followed by Cnt chow diet fed for 4 or 8 weeks; Sham plus CDAA (4W), Sham plus CDAA (8W), Sham followed by CDAA fed for 4 or 8 weeks; Cap plus CDAA (4W), Cap plus CDAA (8W), Cap followed by CDAA fed for 4 or 8 weeks; Sham plus HFD (4W), Sham plus HFD (8W), Sham followed by HFD fed for 4 or 8 weeks; Cap plus HFD (4W), Cap plus HFD (8W), Cap followed by HFD fed for 4 or 8 weeks. For each group, BW and LW were measured, and tissues and blood were collected at 4 and 8 weeks. (B) The efficacy of the neural blockade was confirmed by immunostaining of the nerves with anti-CGRP antibody. Three different sections from each of the five mice in the Cap plus Cnt groups were quantitatively analyzed for the CGRP+ cells using ImageJ software. Data are mean±s.d. (n=15 for each group) *P<0.05, **P<0.01, one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. (C) Time-dependent change of BW. Data are mean±s.d. ***P<0.001 between Sham plus HFD and Cap plus HFD group, two-factor repeated measure ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. (D) LW/BW ratio. Representative images of H&E (E) and Sirius Red (F) staining of the livers. Scale bars: 100 μm. Five different sections from each of the five mice (n=25) in all groups were quantitatively analyzed for fatty infiltration and fibrotic tissue using ImageJ software. The bottom panels in F show hydroxyproline levels in the liver. Data are mean±s.d. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; N.S., not significant. Paired two-tailed Student's t-test.