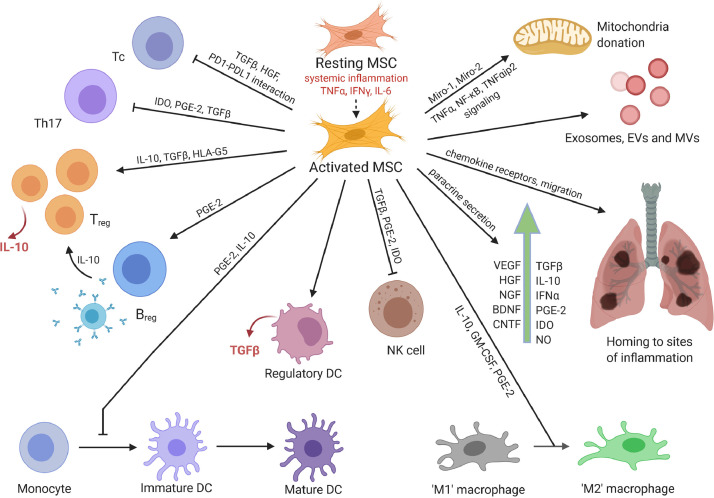
Figure 1.
Immunomodulatory and regenerative effects of MSCs. MSCs assert their immunomodulatory functions by directly or indirectly interacting with innate and adaptive immune cells and via paracrine secretion of cytokines, chemokines and growth factors. Their regenerative effects are attributed to homing to sites of inflammation; release of growth factors, exosomes, EVs and MVs; and direct mitochondrial donation to affected cells. Figure was prepared using BioRender (https://biorender.com/). BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Breg, regulatory B cell; CNTF, ciliary neurotrophic factor; EVs, extracellular vesicles; MVs, microvesicles; NGF, nerve growth factor; NK, natural killer; NO, nitric oxide. (Color version of figure is available online).