Figure 2.
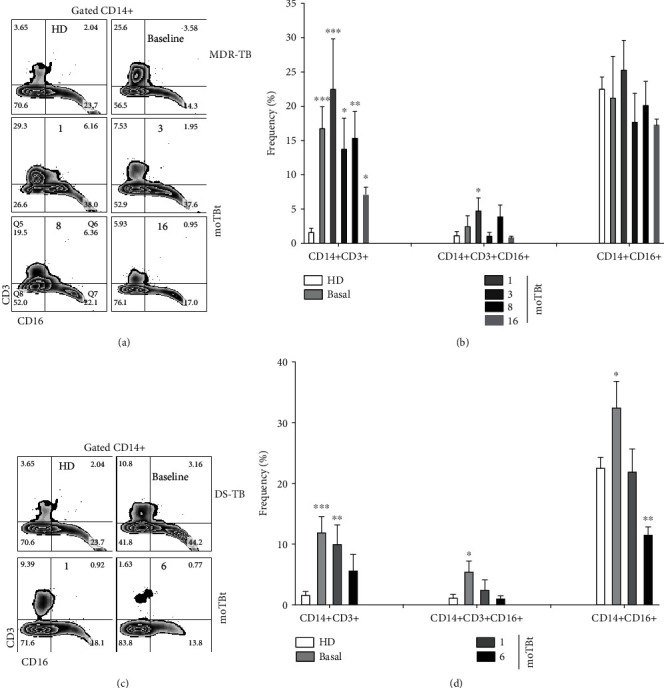
Increased frequency of CD14+CD3+ monocytes during DS-TB and MDR-TB. Representative zebra plots illustrating the gating strategy used to analyze CD3 and CD16 expressions in total CD14+ cells. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) and drug-sensitive tuberculosis (DS-TB) patients were obtained at different time points and employed for phenotypical characterization by flow cytometry (a and c, respectively). (b) Frequency of CD14+CD3+, CD14+CD3+CD16+, and CD14+CD16+ subpopulations in MDR-TB patients (HD: n = 6; MDR-TB: baseline and 1 and 3 moTBt n = 10, 8 moTBt n = 8, 16 moTBt n = 7) (d) Frequency of CD14+CD3+, CD14+CD3+CD16+, and CD14+CD16+ subpopulations in DS-TB patients (HD: n = 6; DS-TB: baseline and 1 moTBt n = 10, 6 moTBt n = 8). Bar graphs show means ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Differences between patient groups and HD at each time point were analyzed using multiple Student's t-test corrected for multiple comparisons using the Sidak–Bonferroni method. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. moTBt: months of antituberculosis treatment.
