Figure 1. NLRP6 expression in mouse lungs following Kp infection.
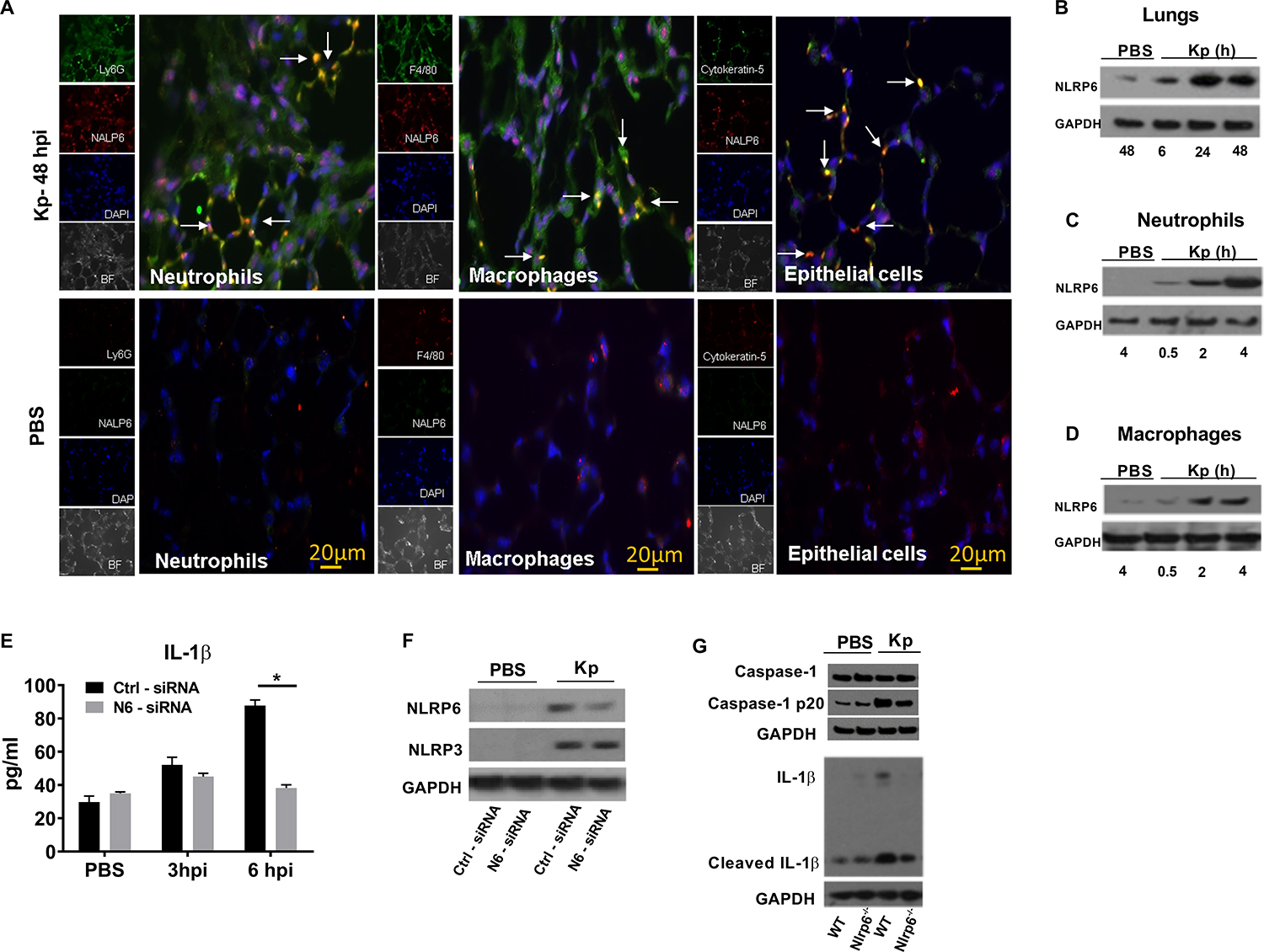
(A) NLRP6 expression at 48 h in lung sections from WT mice following Kp (103 CFU/mouse) or PBS inoculation. In infected group, red staining indicates NALP6 expression. Neutrophils (Ly6G+), macrophages (F4/80+), and epithelial cells (Cytokeratin-5+) are stained green. In PBS group, Green staining shows NLRP6 expression. Ly6G+ neutrophils, F4/80+ macrophages, and cytokeratin-5+ epithelial cells are stained red. This is a representative image of five lung sections with similar results. Original magnification, X 40. Arrows show co-localization. (B) Immunoblotting of NLRP6 in mouse lungs following Kp (103 CFU/mouse) infection at designated time points (hpi). (C–D) Expression of NLRP6 in BMDN and BMDMs at different time points following infection. (E–F) siRNA knockdown of NLRP6 in THP-1 (human macrophage) cells followed by infection with Kp (MOI 1) at indicated time points. THP1 cells (0.5×106) were transfected with NLRP6 or scrambled control siRNA for 48 hours and infected with Kp (MOI 1) for 6 hours. (E) Level of human IL-1β in culture supernatants using triplicate wells. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired t-test. (F) Expression of NLRP6 and NLRP3 proteins in cell lysates after siRNA knockdowns. (G) Immunoblotting of pro-form and cleaved Caspase-1 (p20), and IL-1β in mouse lungs following Kp (103 CFU/mouse) at 48 hpi. Western blots are representative of 3 separate experiments. PBS served as a control. *, p<0.05. BF: bright field, DAPI: 4’, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, hpi: hour post-infection, CFU: colony forming units, MOI: multiplicity of infection.
