Figure 2: TBI-induced alterations in systemic and central immune function.
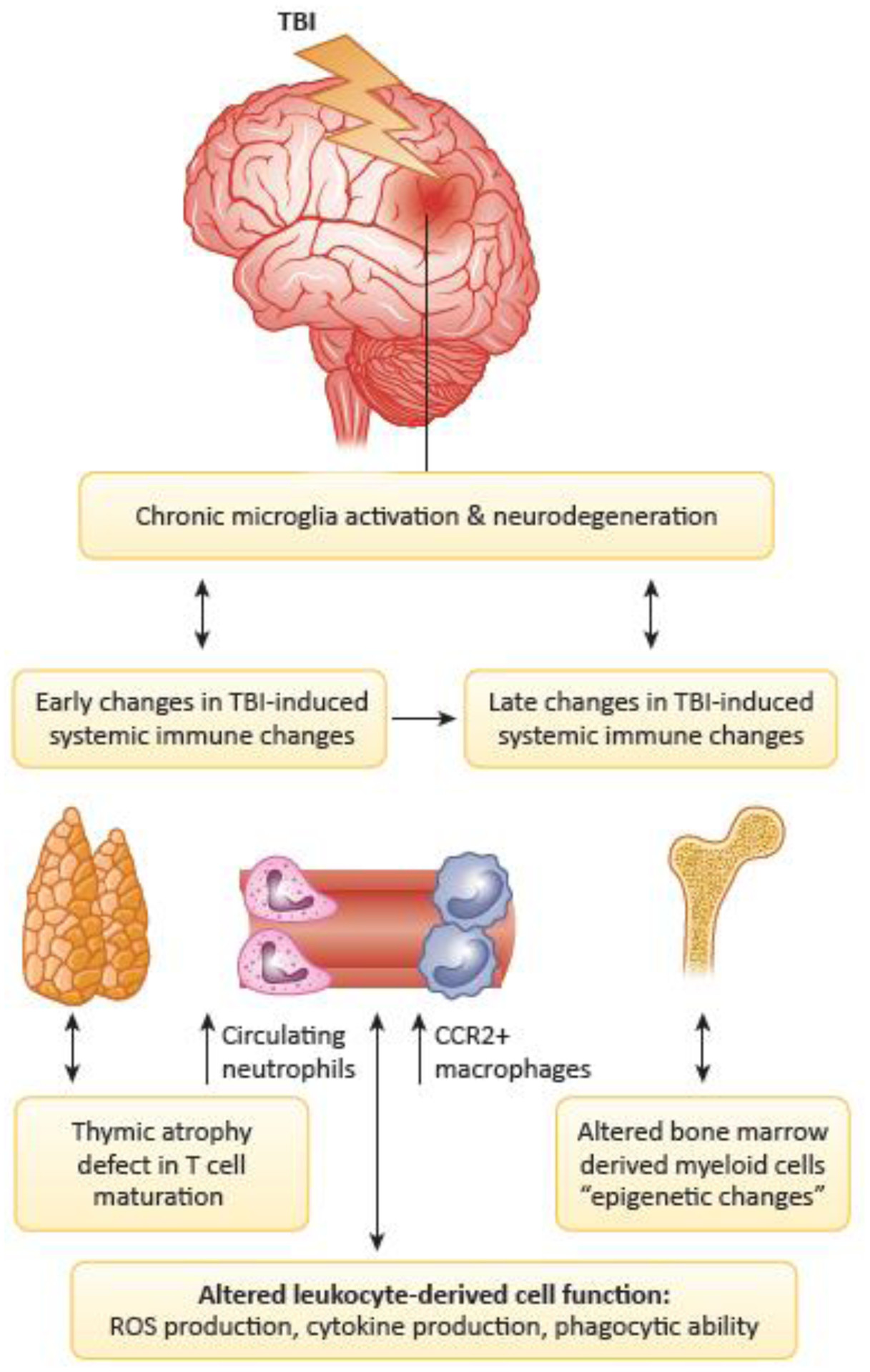
During the early stages of TBI, alterations can emerge in the systemic innate and adaptive immune responses that can in turn alter TBI-induced microglia responses and subsequent neurodegenerative processes. In addition, TBI can induce late changes in systemic immune responses including altered bone-marrow-derived myeloid cell function, which may in turn alter chronic microglial responses and neurodegenerative processes. Abbreviations: Traumatic brain injury (TBI); Reactive oxygen species (ROS); C-C chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2).
