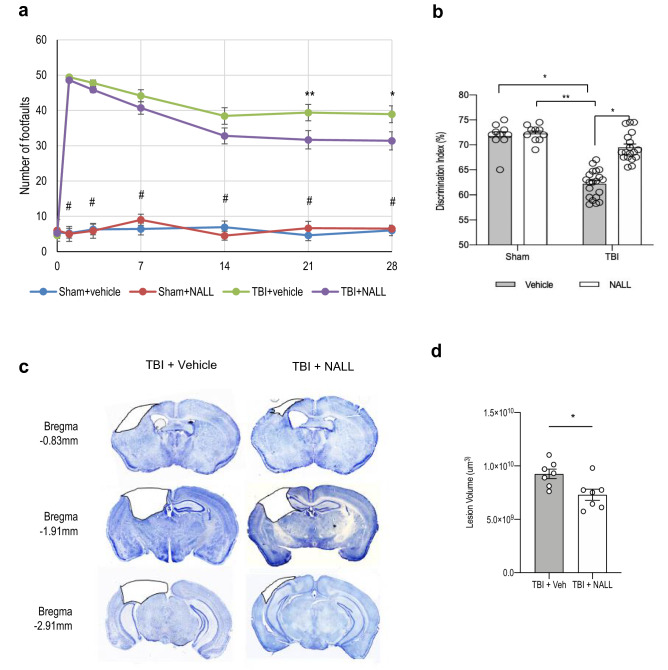
Figure 6.
NALL attenuates motor and cognitive deficits and cortical tissue loss in mice after injury. (a) Sensory motor function was assessed in sham and TBI mice treated with vehicle or NALL using beam walk test. Number of hindlimb foot faults per 50 steps was counted on days 0, 1, 3, 7, 14, 21 and 28 after TBI. Significant injury and treatment effects were detected across all time points except day 0 (prior to injury). (Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test). Both vehicle and NALL-fed sham groups showed significant difference in motor function as compared to the TBI groups fed with NALL or vehicle in all time points except day 0 (#p < 0.0001). Significant improvement in motor function was detected in NALL-fed TBI group as compared to the vehicle-treated TBI mice on days 21 (**p < 0.01) and 28 (*p < 0.05). Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 10 Sham + vehicle, 8 Sham + NALL, 18 TBI + vehicle and 16 TBI + NALL. (b) Novel object recognition (NOR) test was performed on days 24 and 25 after TBI to assess non-spatial memory retention in vehicle or NALL-treated sham or TBI mice. Vehicle-fed TBI mice spent significantly less time with novel object as compared to NALL-treated TBI mice (*p < 0.05, Two-way ANOVA). Time spent with the novel object by the vehicle-treated TBI mice was also significantly less as compared to the vehicle (*p < 0.05) or NALL (**p < 0.01) -fed sham mice. No significant difference was observed between NALL-treated TBI and either of the sham groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 10 Sham + vehicle, 9 Sham + NALL, 20 TBI + vehicle and 18 TBI + NALL. (c) Representative images of lesion volume at 28 days post injury in vehicle and NALL-treated mouse cortices. Images were acquired on Leica DM4000 B TL (BF) microscope and generated using Stereo Investigator software, 2020.2.3 version (MBF Biosciences) and representative black lesion volume outlines seen in the images were traced on Microsoft Powerpoint (Version 16.42). (d) Stereological (Cavalieri method) quantification of lesion volume in vehicle- or NALL-fed injured mouse cortices. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 7/group, *p < 0.05 (Two-tailed Student’s t-test).