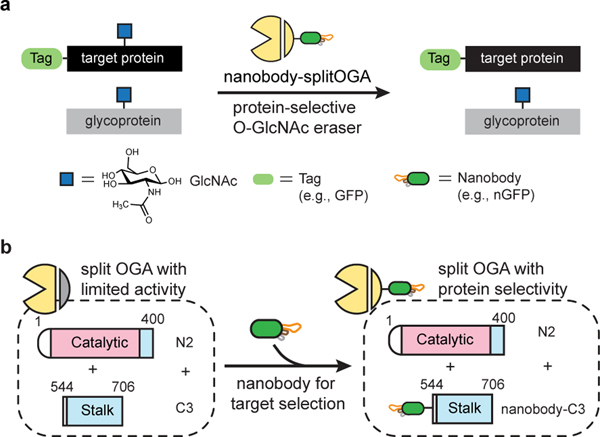
Fig. 1 |. Design and development of a nanobody-directed split OGA for O-GlcNAc removal in a protein-selective manner.
a, Overview of the approach for target protein deglycosylation using a nanobody-directed O-GlcNAc eraser. The nanobody is able to recognize a desired target and redirect the enzyme to remove the O-GlcNAc modification from the target protein. Tags used in this study are GFP, EPEA tag, BC2 tag, and Ubc tag. The corresponding nanobodies are nGFP, nEPEA, nBC2, and nUbc, respectively (see Extended Data Fig. 1c, d). b, Design of split OGA to achieve protein selectivity. OGA was engineered into a split and truncated form with limited inherent substrate activity. Introduction of a nanobody to the split OGA promoted localization to and deglycosylation of the desired target protein. The catalytic domain and stalk domain of split OGA are highlighted in pink and blue, respectively.