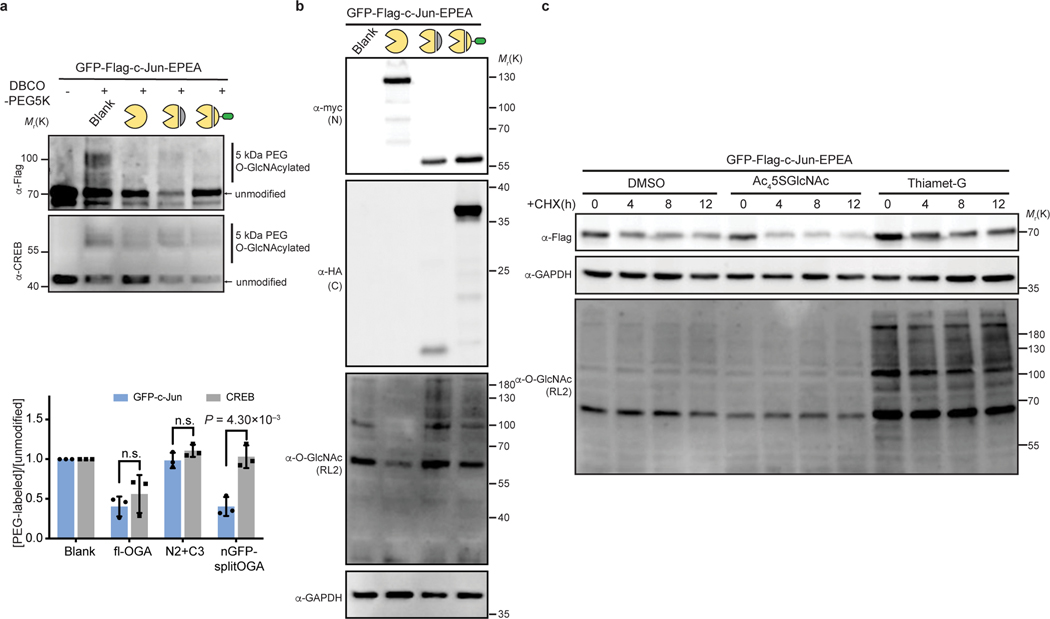
Extended Data Fig. 9. Modulation of O-GlcNAc modification level and validation of its functional contributions on the stability of GFP-c-Jun.
a, O-GlcNAc level on GFP-c-Jun and endogenous CREB were evaluated by the mass-shift assay. GFP-c-Jun was co-expressed with indicated OGA constructs. The intensities of O-GlcNAcylated and unmodified c-Jun and CREB were quantified. Quantification is shown as mean ± s.d. of n = 3 independent biological experiments. All ratios were normalized by the Blank samples. Unpaired two-tailed Student’s t tests were used for statistical analysis. n.s., not significant. b, Whole cell lysates (WCL) were analyzed by immunoblotting assays using the indicated antibodies. Anti-myc and anti-HA blots detect expression of full-length (fl-OGA) or N-terminal fragment, and C-terminal fragment, respectively. The data in a and b are representative of at least three biological replicates. c, The stability of GFP-c-Jun was enhanced by OGA inhibition (Thiamet-G treatment) and impeded by OGT inhibition (Ac45SGlcNAc treatment). HEK 293T cells expressing GFP-c-Jun pre-treated with DMSO or Ac45SGlcNAc or Thiamet-G were incubated with 50 μM CHX for up to 12 h, during which the protein level of GFP-c-Jun and global O-GlcNAcylation level were monitored. Results in c are representative of two biological replicates.