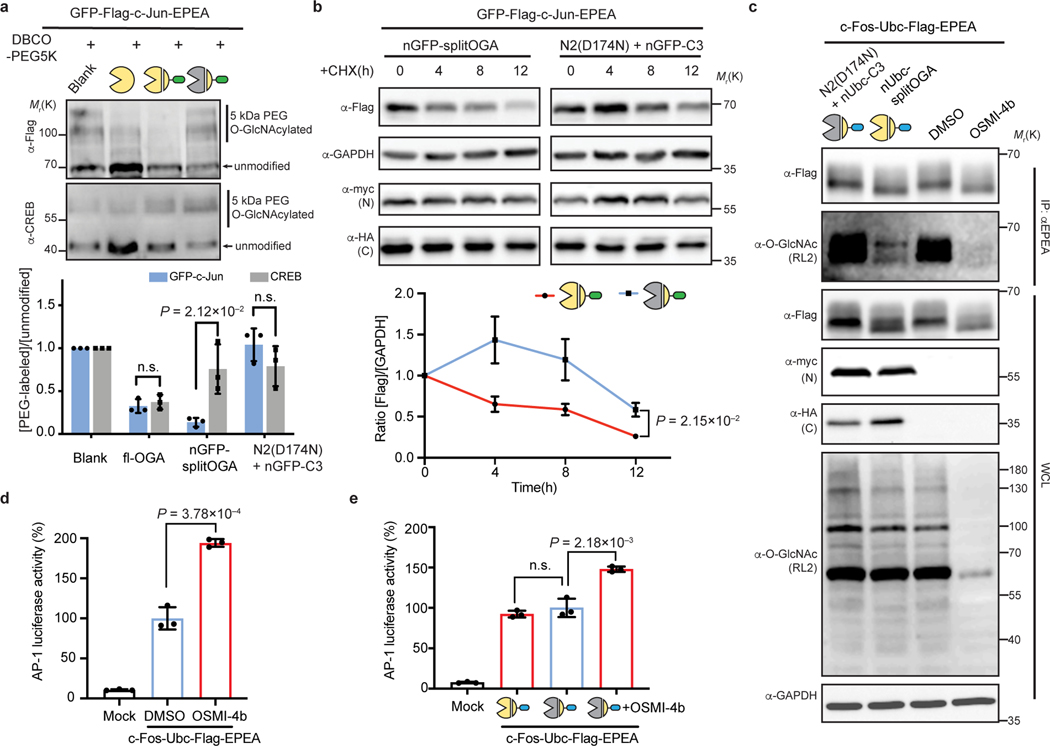
Fig. 5 |. The nanobody-fused split OGA facilitates the functional attribution of O-GlcNAc on c-Jun on protein stability, also O-GlcNAc on c-Fos on AP-1 transcription activity.
a, nGFP-splitOGA can remove O-GlcNAc from GFP-c-Jun selectively. A mass-shift assay was conducted to evaluate the O-GlcNAc level on both GFP-c-Jun and endogenous CREB. b, The stability of GFP-c-Jun is directly related to the extent of O-GlcNAc modification. GFP-c-Jun were co-expressed with indicated constructs in HEK 293T cells. Cells were incubated with 50 μM CHX for up to 12 h and monitored for GFP-c-Jun at different time points. c, nUbc-splitOGA can remove O-GlcNAc from c-Fos-Ubc as OGT inhibitor OSMI-4b, but without causing great reduction of global O-GlcNAc level. Blots are representative of three (a, b) or two (c) biological replicates. d, e, AP-1 luciferase assay showing transcription activity upon OGT inhibition by OSMI-4b (d), or upon the expression of nUbc-splitOGA (e) in c-Fos-Ubc co-transfected HEK 293T cells. Quantitative results are the mean ± s.d. of n = 3 independent experiments, using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t tests for statistical analysis in a, b, d and e. n.s., not significant. WCL, whole cell lysate. Symbols represent corresponding OGA constructs as indicated.