Extended Data Fig. 6. Effects of removing synthetically lethal combinations of ZBPs on FtsZ.
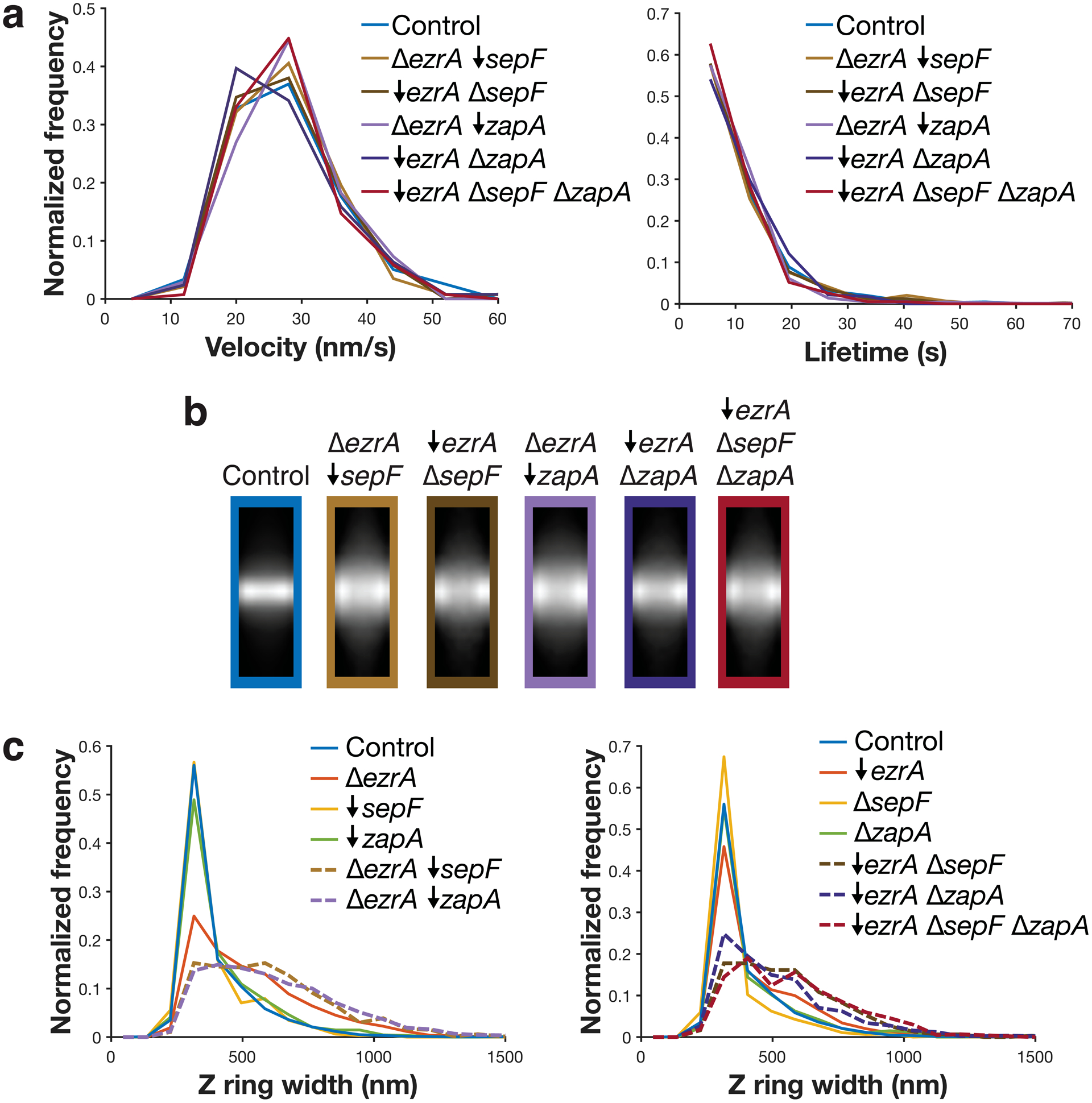
Velocity, lifetime, and Z ring morphology measurements for cells missing each synthetic lethal combination of ZBPs. All synthetic lethal combinations were investigated by a combination of knockouts (indicated by Δ) and depletions (indicated by ↓); depletions were performed by expressing the gene under an inducible promoter until the start of the experiment, then withdrawing the inducer for 7 hours. a Velocity (left) and lifetime (right) of cells missing synthetically lethal combinations of ZBPs are unchanged from control. For velocity measurements, FtsZ-mNeonGreen was induced with 20 μM IPTG for 2 hours, imaged by TIRFM, and then analysed from kymographs. For lifetime measurements, FtsZ-HaloTag was induced with 20 μM IPTG for 2 hours and labelled with 40 pM JF549-HTL. bc Z rings in cells missing synthetically lethal combinations of ZBPs are wider than control cells and cells missing individual ZBPs. Average intensity projections (b) and widths (c) of Z rings in each condition. Z rings were visualized using epifluorescence images of cells expressing FtsZ-mNeonGreen, induced with 20 μM IPTG for 2 hours. Z ring projections were created by averaging >100 Z ring images for each strain. Because ZBPs can be removed by either knockout or depletion, for each strain we compare to the equivalent single mutant knockouts and depletions.
