Extended Data Fig. 1. Cell lengths with fusions for fluorescence microscopy.
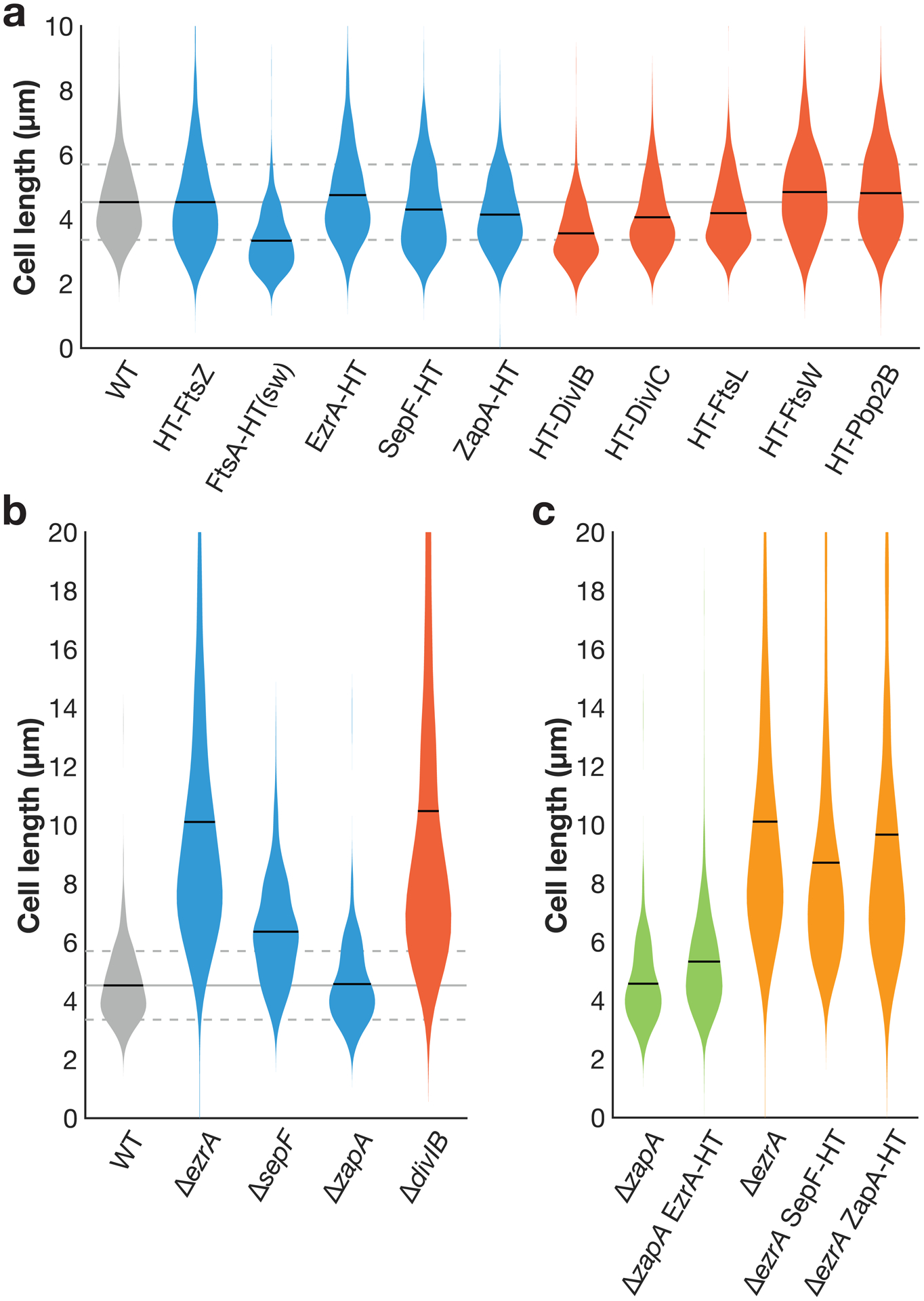
a Cell lengths in strains expressing HaloTag (HT) fusions used in this study. (sw) indicates a sandwich fusion. Cell lengths were measured from confocal microscopy of FM5-95 membrane stained cells. When cell division is inhibited, cell length increases; that cell lengths in each strain are equal to or less than that of wild type (WT) cells indicates that these fluorescent fusions do not strongly inhibit cell division. In some cases where the fluorescent fusion is merodiploid or expressed under inducible control, cells are shorter than WT, as might be expected when components of the cell division machinery are overexpressed. Blue: fusions to early-arriving division proteins, red: fusions to late-arriving division proteins. Gray lines: mean (solid line) ± standard deviation (dashed lines) for WT cell lengths. N>400 cells for each sample. b Lengths of cells with various division proteins knocked out, for comparison with a. We include all knockouts whose lengths can be measured in a straightforward way: ΔftsA cells have severe division defects and are highly elongated (see Extended Data Fig. 10), and the remaining division proteins are essential to avoid lethal filamentation59–62. N>140 cells for each sample. c EzrA and ZapA HT fusions are functional and SepF HT fusion expressed at an ectopic site does not disrupt SepF function. EzrA is synthetically lethal with SepF and ZapA18,29. We therefore knocked out one of these proteins and then expressed our HT fusion to the other protein; if HT fusion induced a critical defect in protein function, this combination will be lethal. Instead, in each case cells remained viable, with comparable lengths to the knockout alone. N>200 cells for each sample.
