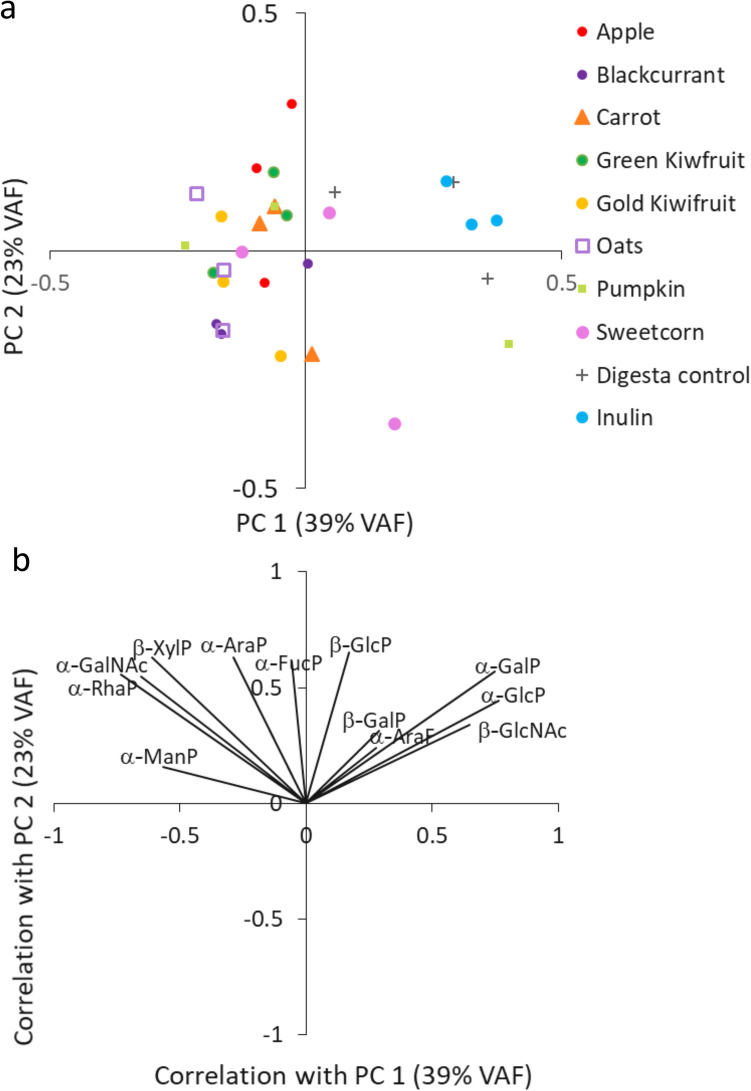
Figure 3.
Principal component analysis plot (a) and the loadings plot (b) demonstrate microbial glycosidase-driven separation of foods and controls after 10 h of fermentation with infants’ faecal inocula. Each substrate was fermented in triplicate. The enzymes included α-arabinofuranidase (α-AraF), α-arabinopyranosidase (α-AraP), α-fucopyranosidase (α-FucP); α-glucopyranosidase (α-GlcP), β-glucopyranosidase (β-GlucoseP), α- and β-galactopyranosidase (β-GalP), α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase (GalNAc), β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (β-GlcNAc), α-rhamnopyranosidase (α-RhaP), α-mannopyranosidase (α-ManP) and β-xylopyranosidase (β-XylP).