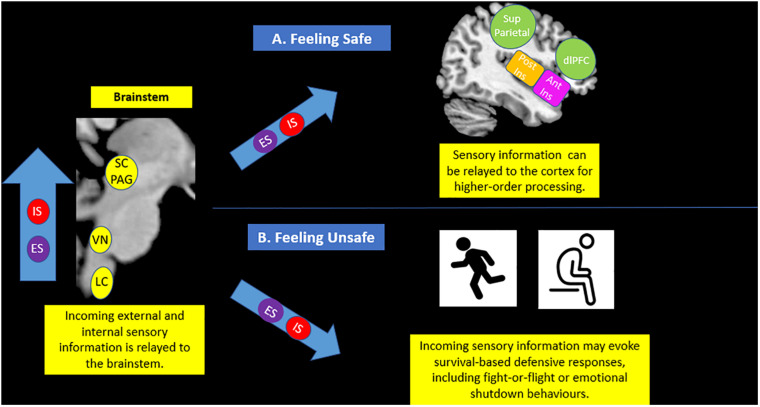
FIGURE 5.
Brainstem sensory processing. The brainstem is responsible for receiving incoming exteroceptive sensations from the external environment (ES) and simultaneous interoceptive affective sensations stemming from within the body (IS). If an individual feels safe (A), it is thought that sensory information can be effectively relayed to areas of the cortex, including the insula and the prefrontal cortex, for advanced processing. However, if an individual feels unsafe (B), incoming sensory information may cause fluctuations in arousal that evoke survival-based active and passive defensive responses, including fight-or-flight and emotional shutdown behaviors. IS (Internal Sensations), ES (External Sensations), SC/PAG (Superior Colliculus/Periaqueductal Gray), VN (Vestibular Nuclei), LC (Locus Coeruleus), Post Ins (Posterior Insula), Ant Ins (Anterior Insula), Sup Parietal (Superior Parietal Cortex), dlPFC (Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex).