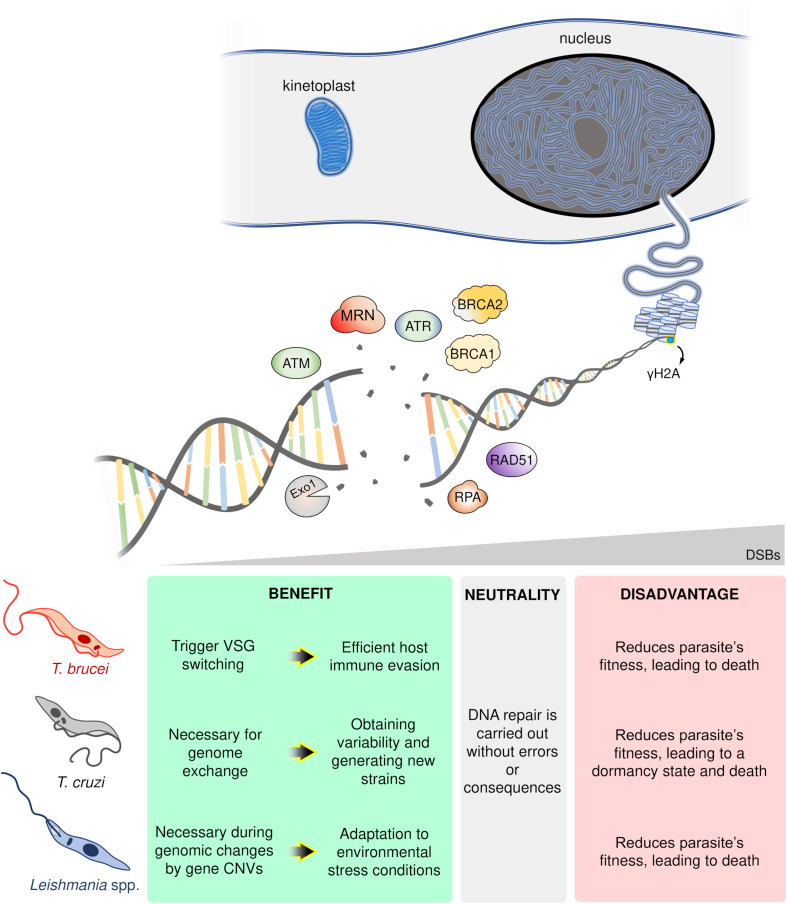
FIGURE 2.
Schematic overview of the possible trypanosomatid cell’s fate in response to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). In a hypothetical trypanosomatid, several players act in an orchestrated way in response to DSBs. However, according to the number, location, cell cycle phase, and DNA repair capacity of the cell, these lesions can trigger different consequences: advantages (green box), neutrality (gray box), or disadvantages (red box). ATM, ataxia telangiectasia mutated; ATR, ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related; MRN, MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 complex; Exo1, Exonuclease 1; RPA, Replication protein A; BRCA1-2, Breast cancer 1–2; Rad51, Recombinase involved in homologous recombination; γH2A, phosphorylated histone H2A.