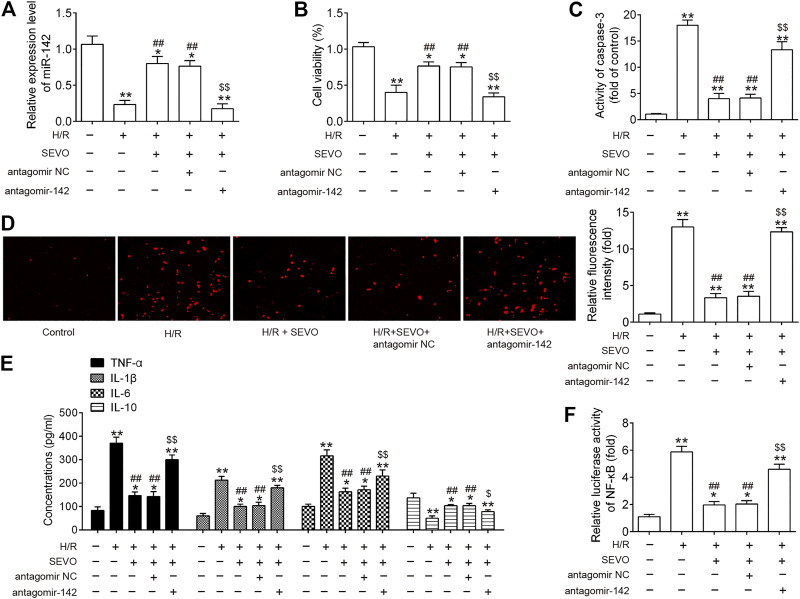
FIGURE 8.
Sevo postconditioning exerts its protective effect against hepatic I/R injury through inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in vitro. Cells were transfected with antagomir-NC/antagomir-142 (100 nM) for 24 h, and then subjected to H/R for 6 h. Before hypoxia treatment, cells were placed in a semi-airtight container and 2% sevoflurane was used for 2 h of pre-treatment. (A) The expression levels of miR-142 was measured by qRT-PCR. (B) Cell viability was determined by CCK-8 assay. (C) The activity of caspase-3 was measured by a commercial kit. (D) ROS production was assessed by DCFH-DA assay. (E) The inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10, were evaluated by ELISA assays. (F) Luciferase activity of NF-κB was quantified using the Promega luciferase assay kit on a luminometer. All data were measurement data which were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and analyzed by one-way analysis of variance. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. Control group; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. H/R group; $ p < 0.05, $$ p < 0.01 vs. H/R + Sevo + antagomir NC group.