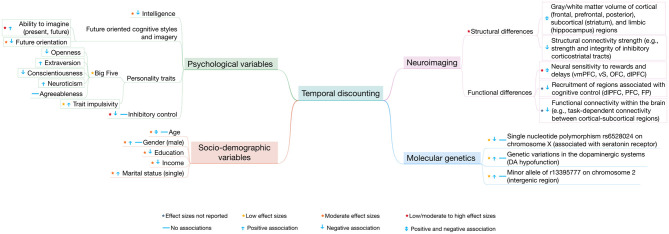
Figure 2.
Summary of the associations between temporal discounting and socio-demographic, psychological, neuroimaging, and molecular genetic variables. The figure in a simplified way summarizes how the different variables relate to (steep) temporal discounting. However, the relation of these variables to temporal discounting is far from being so simple and isolated (as it may appear in the figure) as these variables often interact with each other. Low effect sizes are considered d (or r) < 0.15; moderate effect sizes are considered 0.15 ≤ d (or r) ≤ 0.35; high effect sizes are considered d (or r) > 0.35. vmPFC, ventromedial prefrontal cortex; vS, ventral striatum; OFC, orbitofrontal cortex; dlPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; PFC, prefrontal cortex; FP, frontal pole; DA, dopamine.