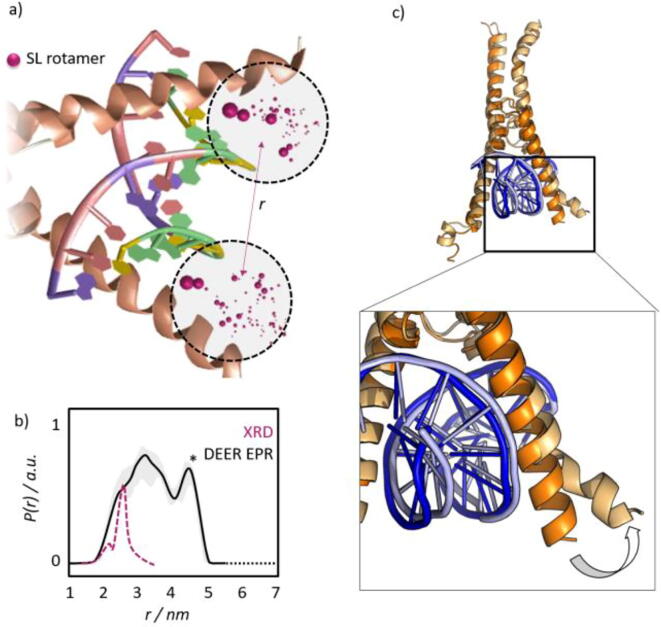
Fig. 5.
Assessment of TF conformations in their DNA-bound state by EPR nanoscale distance measurements. a) Rotamer distributions predicted for two spin labels attached to the DNA-binding domain of MAX:MAX. The purple dots indicate the conformational freedom of the nitroxide (MTSL) labels attached to the transcription factor. b) The experimental distance distribution obtained by EPR (black) compared to the distribution computed from the crystal structure through a rotamer analysis (purple). Only the most compact state is represented by the XRD-derived structure, while a broader conformational ensemble is found in solution by EPR. c) The conformational sampling of DNA-bound MAX:MAX found in MD simulations confirmed that the DNA-binding domain opens and closes continuously around the bound DNA-ligand. This conformational tuning results in the broad experimental distance distribution shown in panel b. (adapted from reference [63] with permission of the publisher.) (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)