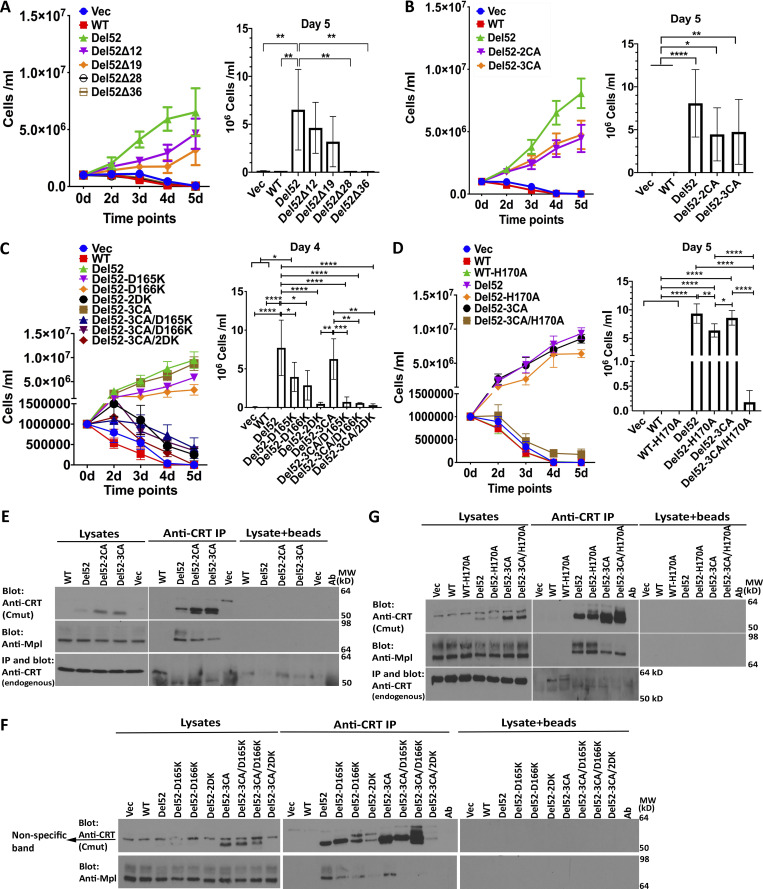
Figure 7.
Large C-domain truncations or combined N-domain and C-domain dimer interface mutations are required to abrogate CRTDel52-mediated cell proliferation. (A–D) Cytokine-independent proliferation of Ba/F3-Mpl cells expressing full-length untagged CRTWT, CRTDel52, indicated CRTDel52 mutants, or control cells (Vec). Data are averaged from three separate viral transductions of Ba/F3-Mpl cells and a total of 5 independent proliferation experiments (A), eight separate viral transductions of Ba/F3-Mpl cells and a total of 10–13 independent experiments (B), two to three separate viral transductions of Ba/F3-Mpl cells and a total of 3–6 experiments (C), or two separate retroviral transductions of Ba/F3-Mpl cells and a total of 5 independent experiments (D). Mean ± SEM is shown, with statistical significance assessed via ordinary one-way ANOVA from the indicated days of proliferation assay. Statistically significant means are indicated as *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; and ****, P < 0.0001. (E–G) Lysates from Ba/F3-Mpl cells expressing indicated constructs or control cells expressing Mpl alone (Vec) were directly loaded for immunoblotting analyses (labeled as lysates) or immunoprecipitated with anti-CRT(Cmut) antibody (for CRTDel52 and its variants) or with anti-CRT(Thermo) antibody (for CRTWT), and subsequent immunoblotting was undertaken with the indicated antibodies. Results are representative of three (E and F) or four (G) independent experiments. Nonspecific interactions in the absence of primary antibody are shown by the lysate + beads lanes. Ab, antibody; MW, molecular weight.