Figure 1.
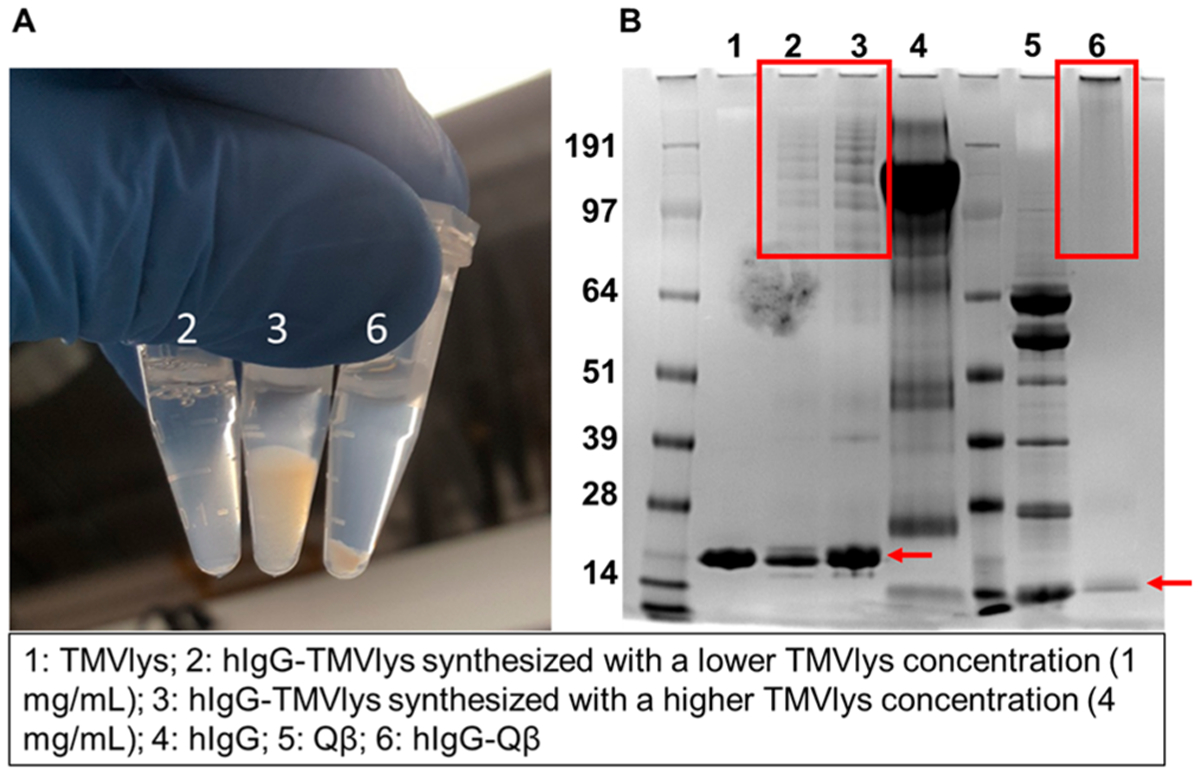
Chemical conjugation of antibodies to VNPs/VLPs using amine/thiol-reactive chemistries. (A) Photograph of antibodies conjugated to TMVlys and Qβ via amine and thiol-reactive chemistries. All particles are heavily agglomerated as evident by the formation of pellets. (B) Corresponding SDS-NuPAGE gel electrophoresis image. Red boxes highlight multiple high molecular weights bands for TMV-antibody conjugating indicating conjugation of multiple and/or cross-linking between antibodies and coat proteins. In the case of Qβ, the conjugated bands could not be resolved indicating high degree of cross-linking. Red arrows point to the coat proteins of TMVlys (~17 kDa) and Qβ (~14 kDa). It should be noted that a reducing agent was not added in the sample preparation; this explain the multiple banding for the Qβ samples showing coat proteins and dimers and multimers formed through disulfide bridges. Green arrows point to the light chain (~25 kDa) and heavy chain (~ 50 kDa) as well as the assembled IgG (again reducing agents were not added during sample preparation).
