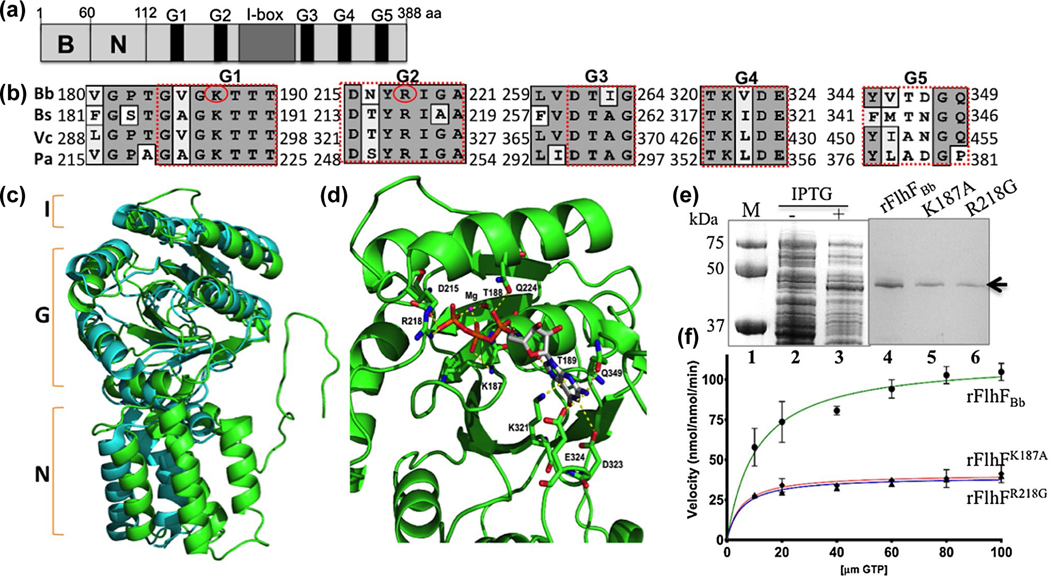
FIGURE 1.
BB0270 is an FlhF-like GTPase. (a) Domain structure of BB0270 (FlhFBb). The positions of the N-terminal basic (B), the central (N) domains, the conserved nucleotide-binding elements (G1-G5) as well as the I-box in FlhFBb are indicated. (b) Multiple sequence alignments of different FlhF G-domains. The numbers represent the positions of aa in the FlhF proteins of B. burgdorferi (Bb), B. subtilis (Bs), V. cholerae (Vc) and P. aeruginosa (Pa). Red circles indicate two residues that are replaced by site-directed mutagenesis. The GenBank accession numbers for these proteins: FlhFBb (WP_002556869), BsFlhF (WP_003231945), VcFlhF (WP_001881782), and PaFlhF (WP_003114281). The alignment was carried out using the program MacVector 10.6. (c) Homology modeling analysis shows that FlhFBb shares a similar structural topology to BsFlhF. The figure was generated by homology modeling using BsFlhF (PDB ID: 2PX3) as a template. Green is FlhFBb and cyan is BsFlhF. (d) FlhFBb harbors a conserved GTP and Mg2+ binding site. This is a close up view of the GTP and Mg2+ binding site of FlhFBb. The map was generated by homology modeling using BsFlhF (PDB ID: 2PX3) (Bange, Petzold, Wild, Parlitz, et al., 2007) as a template. The conserved aa involved GTP and Mg2+ binding sites were as labeled. (e) SDS-PAGE analysis of GST-FlhFBb recombinant proteins expressed in E. coli. Lane 1, molecular marker; lane 2 and lane 3, E. coli whole cell lysates induced without or with IPTG; lane 4–6, purified wild type (rFlhFBb) and two mutated (rFlhFK187A and rFlhFR218G) recombinant proteins. (f) Michaelis-Menten plots show kinetic plots for the GTPase activity of purified rFlhFBb and two variant recombinant proteins. The final data were expressed as means ± standard deviations (SD) of triplicates from three independent assays. The detail enzymatic parameters are present in Table 1