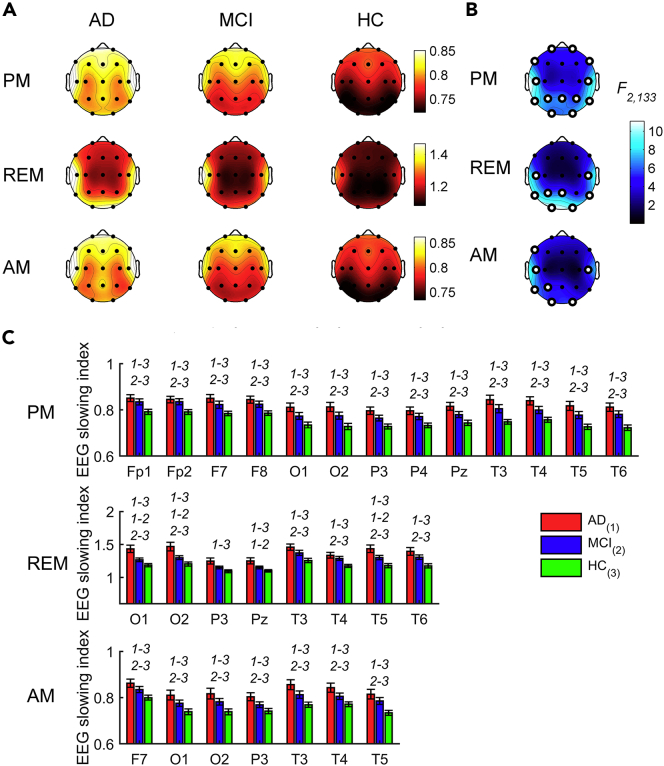
Figure 4.
The EEG slowing during REM sleep and wakefulness in AD, MCI, and HC groups
(A) Topographic maps of the EEG slowing index [(delta + theta)/(alpha + sigma + beta)] during evening wakefulness (PM, first row), REM sleep (second row), and morning wakefulness (AM, third row) in AD (first column), MCI (second column) and HC (third column) groups. The topographic maps are scaled between minimal and maximal values of the three groups within each condition.
(B) Statistical maps (F-values) of the one-way ANOVAs (AD vs. MCI vs. HC) on the EEG slowing index in each condition. Maps are scaled between minimal and maximal F-values across the statistical comparisons in all conditions. White dots represent significant statistical differences, according to the FDR correction (p ≤ 0.0102). See also Table S5.
(C) Histograms of the EEG slowing index (mean ± SEM) in AD (red), MCI (blue) and HC (green) groups at the cortical sites showing a significant between-groups difference in the one-way ANOVAs for each condition. y axis of histograms has non-zero origin to magnify standard errors visibility. The groups with significant differences in the post hoc pairwise comparisons by two-tailed unpaired t test (p ≤ 0.05) are reported by numerical code (1: AD, 2: MCI, 3: HC).