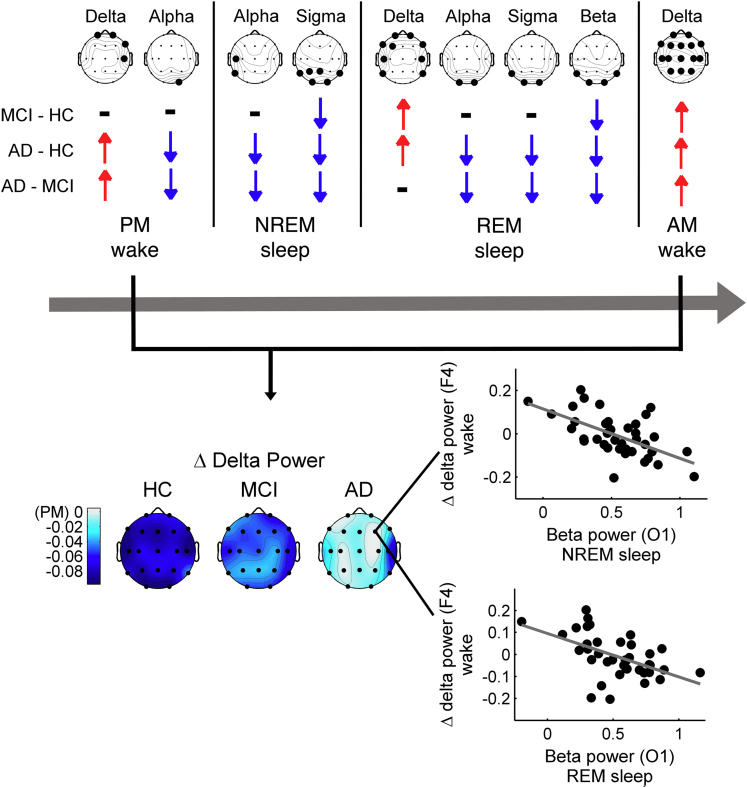
Figure 7.
Summary of the topographic and frequency-specific EEG features of cortical activity during wakefulness and sleep in MCI and AD
Topography of the frequency-specific significant differences in cortical activity in MCI and AD as compared to HC (one-way ANOVAs, p ≤ 0.0102) during evening wakefulness, NREM and REM sleep, and morning wakefulness (upper). The direction of the difference in the pairwise comparisons is given by the red and blue arrows representing significant increased and decreased cortical activity (two-tails unpaired t-tests, p ≤ 0.05) in MCI and AD compared to HC and in AD compared to MCI, respectively. The gradual disappearance of the changes in delta power between pre-sleep and post-sleep wakefulness EEG from HC to AD condition (bottom) is also shown. The maps represent AM log10(Delta power) – PM log10(Delta power) differences for HC, MCI, and AD groups. The negative values of the blue scale indicates that delta power decreases after sleep. The scatterplots show the linear correlation among this delta power change at a frontal representative site (F4) and the high-frequency activity during NREM and REM sleep at a posterior representative site (O1) in the AD group. F4 and O1 derivations were respectively chosen as representative for delta power changes in waking EEG and posterior beta power activity during sleep since they showed the highest correlation in the analysis reported in Figure 3C.