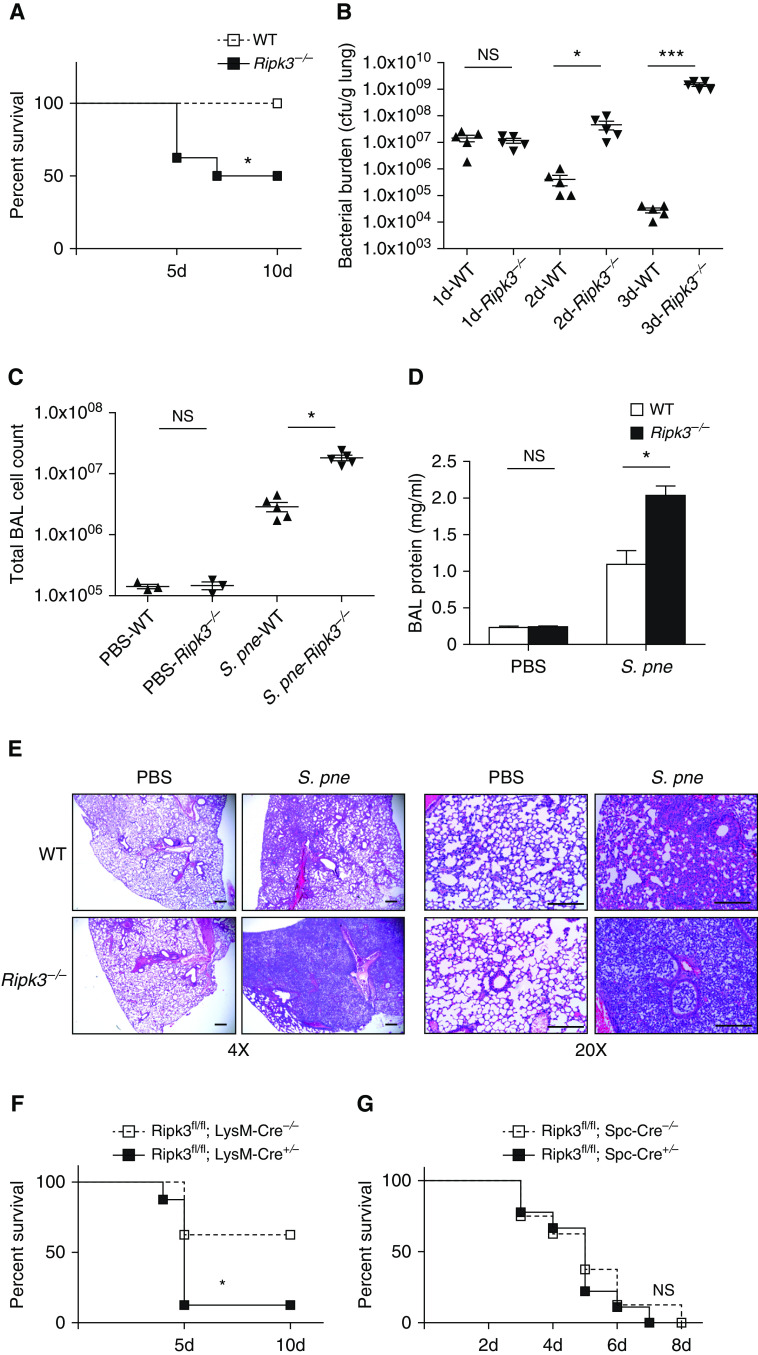
Figure 2.
RIPK3 deficiency leads to worse outcome during S. pne infection. Mice were intranasally instilled with S. pne (ATCC 6303) or PBS. (A) Survival study showed that Ripk3−/− mice were more susceptible to S. pne infection than WT mice (n = 10 for each group). *P < 0.05 by Mantel Cox test. (B) Pulmonary bacterial burden of WT or Ripk3−/− mice at indicated times after infection (n = 5 for each group). (C and D) Total cell counts and protein quantification in BAL fluid of WT or Ripk3−/− mice at Day 3 after infection (n = 3 PBS; n = 5 S. pne). *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001 by one-way or two-way ANOVA test. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. (E) At 3 days after infection, mouse lungs were harvested for histology. Representative photomicrographs (hematoxylin and eosin stained) taken from each group were shown. Scale bars, 20 μm. (F) Survival study of Ripk3fl/fl; LysM-Cre−/− or Ripk3fl/fl; LysM-Cre+/− mice (n = 10 for each group). *P < 0.05 by Mantel Cox test. (G) Survival study of Ripk3fl/fl; Spc-Cre−/− or Ripk3fl/fl; Spc-Cre+/− mice (n = 10 for each group). Technical and biological replicates for infection experiments, N = 10. Experiments were repeated at least three times, with representative findings shown. NS = no significant difference.