Figure 6.
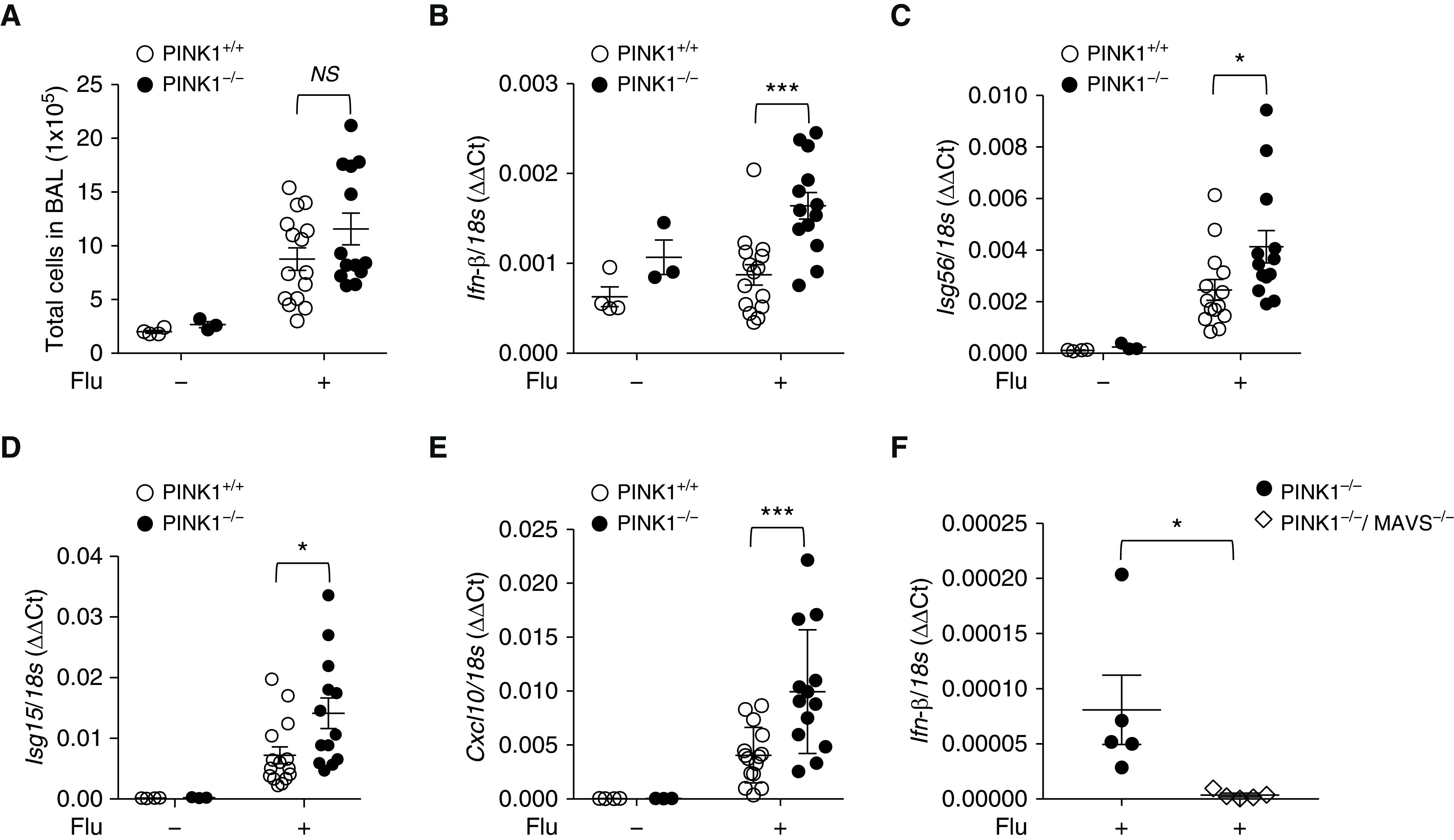
In vivo functional significance of PINK1/MAVS in influenza-infected mouse model. (A–E) 100 plaque-forming units of A/PR8/34 influenza (equivalent to 0.5 median lethal dose in C57BL/6J mice) was administered through intranasal aspiration to WT and PINK1−/− mice. Experimental groups were composed of control WT (n = 3), control PINK−/− mice (n = 4), influenza-infected WT mice (n = 15), and influenza-infected PINK1−/− mice (n = 13). The lysates of total lung tissues were obtained from the mice at Day 5 after influenza infection. (A) Total cell counts of the BAL fluid were evaluated. (B–E) The mRNA levels of Ifn-β (B), Isg56 (C), Isg15 (D), and Cxcl10 (E) were analyzed by quantitative PCR. Readers may view the uncut gels for E in the data supplement. (F) A separate in vivo experiment was undertaken in which experimental groups were composed of influenza-infected PINK1−/− mice (n = 5) and PINK1−/−/MAVS−/− mice (n = 5). The lysates of total lung tissues were obtained from the mice at Day 5 after influenza infection. The mRNA level of Ifn-β was analyzed by quantitative PCR. Means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001. Flu = influenza virus; NS = not significant.
