Figure 2.
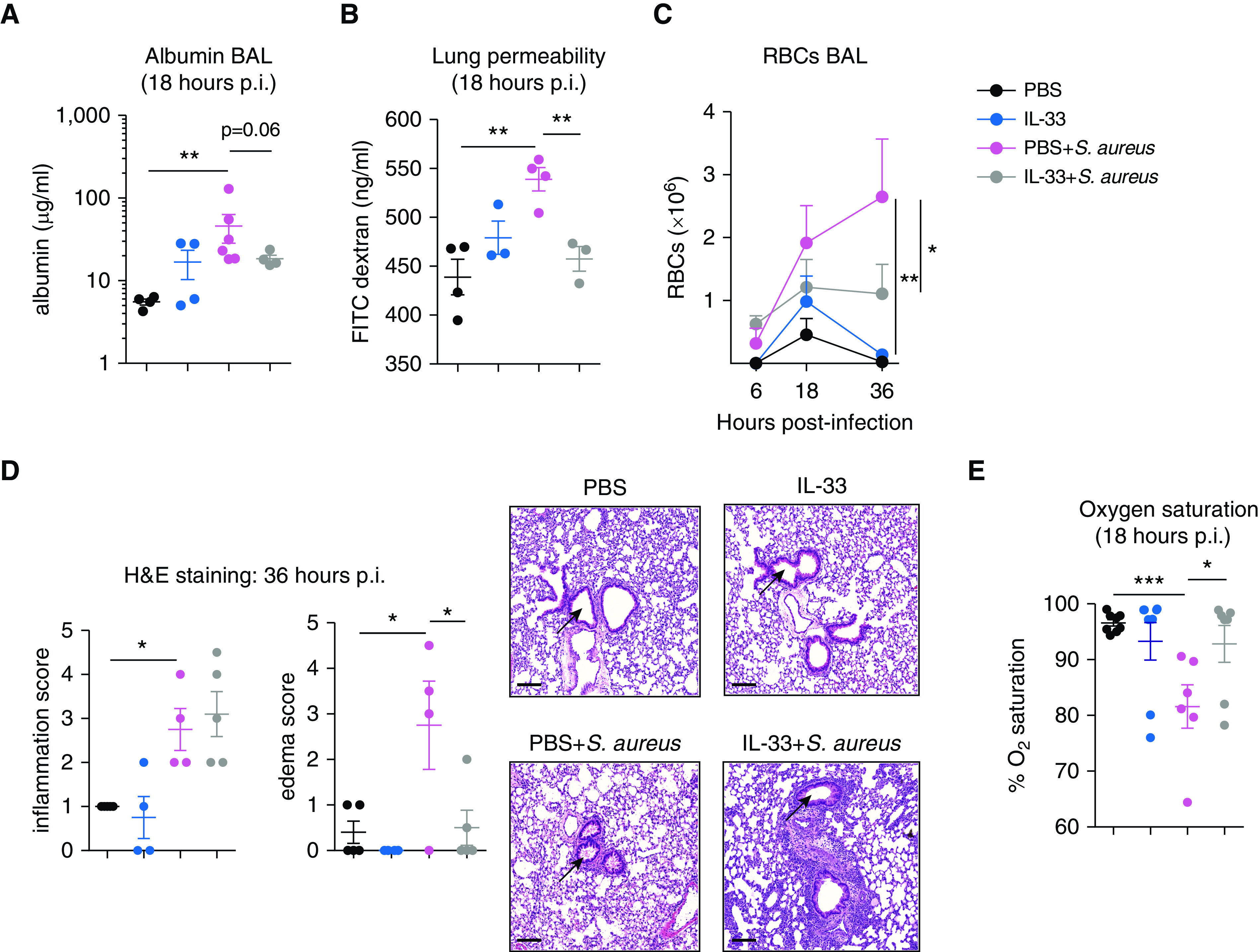
IL-33 pretreatment reduces S. aureus–induced lung injury. C57BL/6 mice were treated i.t. with PBS, IL-33, PBS + S. aureus, or IL-33 + S. aureus. (A) BAL fluid albumin was measured at 18 hours p.i. (B) Quantification of lung permeability using FITC–dextran leakage from alveoli into serum at 18 hours p.i. Pulmonary edema was quantified using (C) flow cytometry measurement of BAL fluid red blood cell (RBC) counts or (D) H&E staining of lung sections with arrows indicating the area assessed for edema within the airways. RBCs were measured in the BAL fluid at 6, 18 and 36 hours p.i. and defined as single cells, live CD45−Ter119+FSClo. (E) Oxygen saturation was measured in live, anesthetized mice at 18 hours p.i. for 10 minutes using the MouseOx Plus system. For A–C, representative graphs of two experiments with sample sizes of three to six per group are shown. For E, two experiments were pooled, with total sample sizes between six and eight per group. For C, statistical significance was determined using a two-way ANOVA with a Tukey post hoc test, whereas for A, B, D, and E, significance was determined using an unpaired t test. Scale bars, 100 μm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. H&E = hematoxylin and eosin.
