Figure 7.
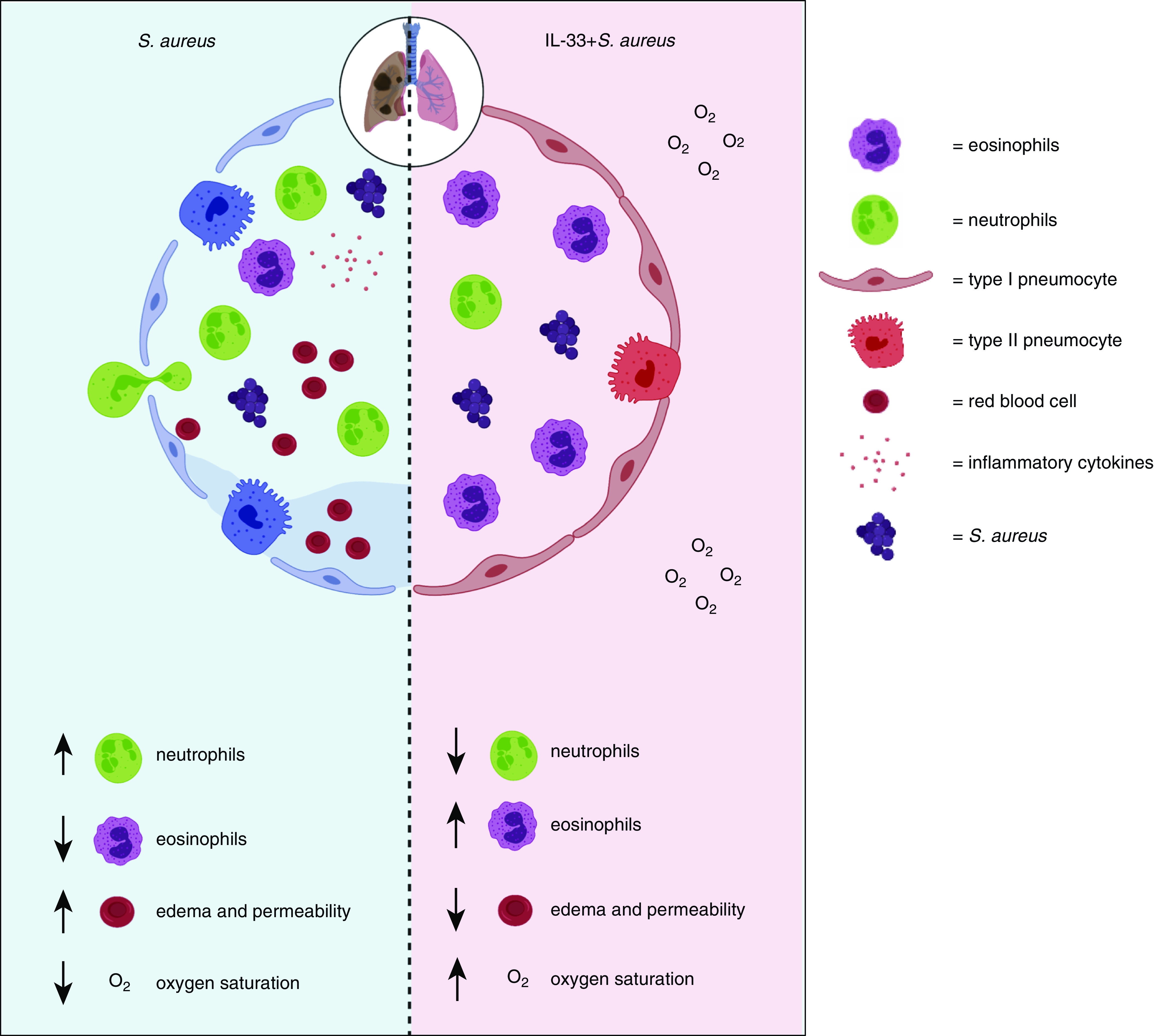
IL-33–mediated eosinophilia protects against lethal S. aureus pneumonia by inhibiting lung injury, with up arrows indicating an increase and down arrows indicating a decrease of the indicated feature. During S. aureus–induced pneumonia, neutrophils extravasate from the blood and interstitium into alveoli early during the immune response to promote bacterial clearance. However, neutrophils can also cause tissue damage, resulting in destruction of epithelial cells lining the alveoli. This causes infiltration of inflammatory cytokines, increased pulmonary edema, and finally hypoxemia. Our study demonstrates that IL-33–mediated eosinophilia inhibited induction of airway inflammatory cytokines, neutrophilia, pulmonary edema, lung permeability, and hypoxemia.
