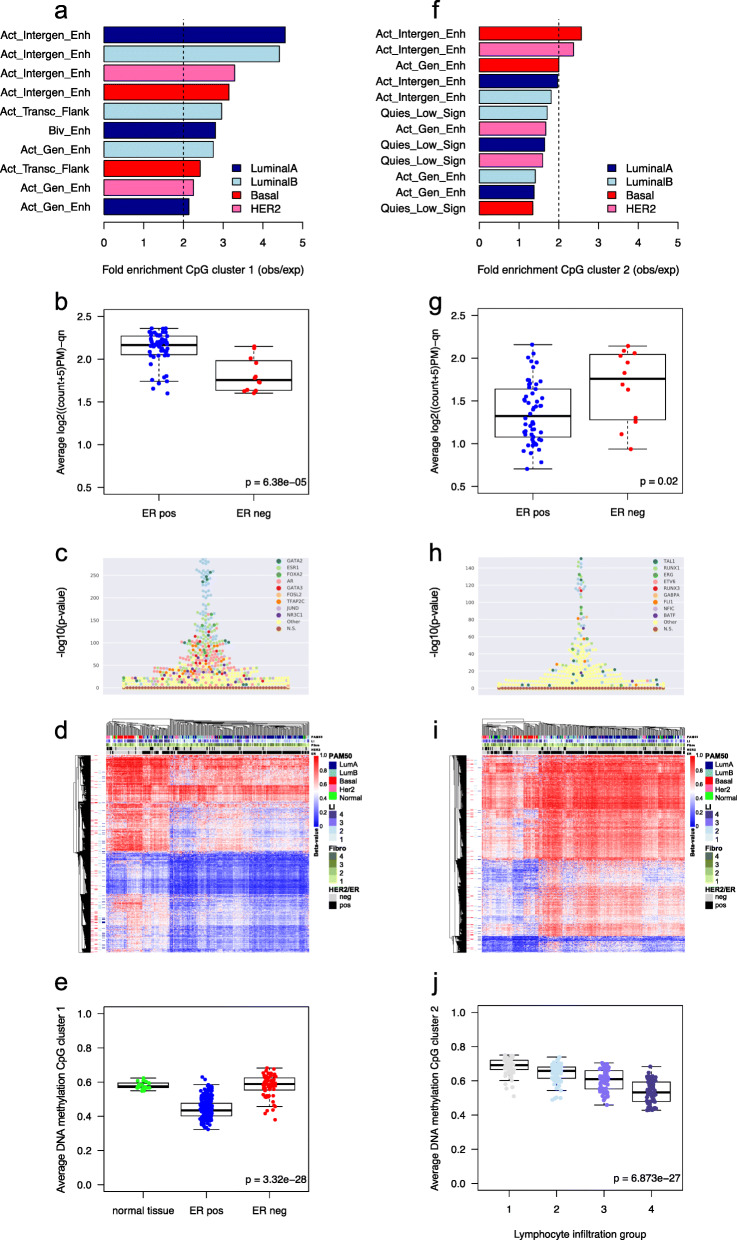
Fig. 2.
Functional annotation of the CpG clusters. a Genomic location enrichment of mimQTL CpGs in cluster 1 according to ChromHMM data from cell lines representing different breast cancer subtypes [37]. Only regions with fold-enrichment > 2 are shown. Active Genic Enhancer = Act_Gen_Enh, Active Transcription Flanking = Act_Transc_Flank, Bivalent Enhancer = Biv_Enh, Active Intergenic Enhancer = Act_Intergen_Enh, observed = obs, expected = exp. b Average normalized counts per tumor sample for all ATAC-seq peaks mapped to CpGs of cluster 1 (TCGA data). c Beeswarm plot showing enrichment of TF binding sites (−(log10(p value) using Fisher’s exact tests) on the y-axis for CpGs of cluster 1 (n = 14,040) according to UniBind [40]. TF names of the top 10 enriched TF binding sites data sets are provided with dedicated colors. Data sets for the same TFs are highlighted with the corresponding colors. d Heatmap showing hierarchical clustering of tumor methylation levels of CpG cluster 1 (n = 14,040) in the Oslo2 cohort (CpGs in rows and tumors in columns). Tumors are annotated according to PAM50 molecular subtypes; lymphocyte infiltration (LI) quartile groups 1(low)–4(high); fibroblast infiltration quartile groups (Fibro): 1(low)–4(high); human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status; estrogen receptor (ER) status. CpGs are annotated according to overlap with regions annotated as “Active Intergenic Enhancer” from ChromHMM of subtype-specific cell lines [37]; Her2 (pink), Basal (red), LumB (light blue), and LumA (dark blue). e Boxplot showing average DNA methylation of CpGs from cluster 1 in normal breast tissue (n = 17), ER-positive (pos; n = 223) and ER-negative tumors (neg; n = 60) of the Oslo2 cohort. f Enrichment of mimQTL CpGs in cluster 2 according to ChromHMM data. Quiescent_Low signals = Quies_Low_Sign. g Average normalized counts for ATAC-seq peaks mapped to CpGs of cluster 2. h Enrichment of TF binding sites for CpGs of cluster 2 (n = 12,706). i Hierarchical clustering of tumor methylation levels of CpG cluster 2 (n = 12,706). j Boxplot showing average DNA methylation of cluster 2 CpGs when Oslo2 tumors were separated into lymphocyte infiltration quartile groups from low (1) to high (4). Wilcoxon rank-sum p values (two-group comparisons) and Kruskal-Wallis p values (three or more groups) are indicated